You Want 4 GB RAM on Your Notebook?
Synchronous vs. asynchronous Dual Channel
Many modern notebook chipsets, including all current Intel models, support synchronous dual channel operation, which means that both or all four memory modules have to be equal. Most chipsets also support asynchronous dual channel, which allows the user to mix a 1 GB DIMM and a 2 GB DIMM in order to reach a total RAM capacity of 3 GB and still run dual channel mode. While this doesn’t deliver the full performance that can be achieved in dual channel mode, it’s still faster than single channel, and we haven’t heard of issues with it. If you intend to upgrade your 1 GB of RAM by installing a 2 GB DIMM, there is nothing that stands in your way. In a worst case scenario your system will be running in single channel memory mode, which will result in a very small performance penalty.
Test Notebook: Dell Latitude D630
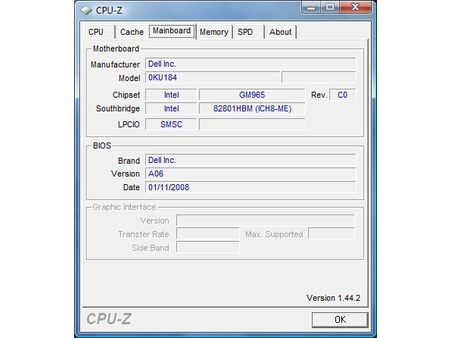
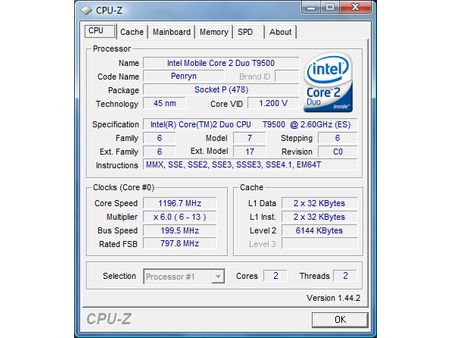
We used a modern notebook based on Intel’s 45 nm mobile processor, the Core 2 Duo T9000 family. The Dell latitude utilizes the entire Intel Centrino platform, including the GM945 mobile chipset, a Core 2 Duo T9500 (2.6 GHz) and the 4945AGN wireless solution. Since this is a business notebook, it doesn’t come with a discrete graphics solution, rather utilizing the integrated graphics unit provided by the GM965 Express chipset. Gamers won’t like this very much, but the focus of this article is the impact more memory has on battery runtime, and a graphics chip will contribute to emptying your battery quicker than a notebook with slower but more efficient integrated graphics.
The notebook also has a Hitachi TravelStar 7K160 hard drive, which isn’t a very efficient model, but offers maximum performance. The 14” WXGA+ display isn’t state of the art, but is probably a common choice today.
Since we had a good experience with Futuremark’s MobileMark 2007 and this particular notebook, we used Windows Vista Ultimate with Service Pack 1, and we patched MobileMark with patch 3 as well to be sure we have the latest software platform.
Dell utilizes a GM965 chipset (Santa Rosa) for its Latitude D630.
The Core 2 Duo T9000’s idle clock speed is 1,200 MHz, which comes from the FSB800 200 MHz base clock speed times a base multiplier of 6.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Synchronous vs. asynchronous Dual Channel
Prev Page Some Memory Basics Next Page Upgrading the Latitude D630