PC Interfaces 101
ATA/133 (Parallel ATA, UltraDMA/133 Or E-IDE)
This is the parallel bus for data transfer from hard disks and optical drives (CD and DVD) also known as Parallel ATA, to contrast with Serial ATA. The latest version features an 40 pin, 80 wire ribbon cable to connect motherboards to drives. Each such cable can support up to a maximum of two devices, with one drive on a cable configured as the master drive, and the other as the slave. This setting is normally handled by a small jumper block somewhere on the drive.
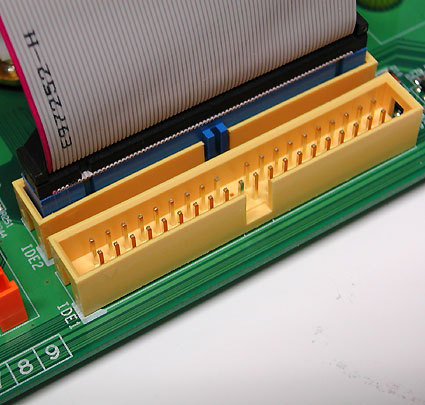
IDE ribbon cable
Connecting to a DVD drive: the red stripe on the ribbon cable should always be next to the power cable (to the right of the white peripheral connector in this photo)
ATA/133 connector to a classical 3.5" hard disk (below) and a 2.5" model (above)
Those who want to install a 2.5" notebook hard disk in a typical desktop PC - if only for data synchronization - can use an adapter like this one.
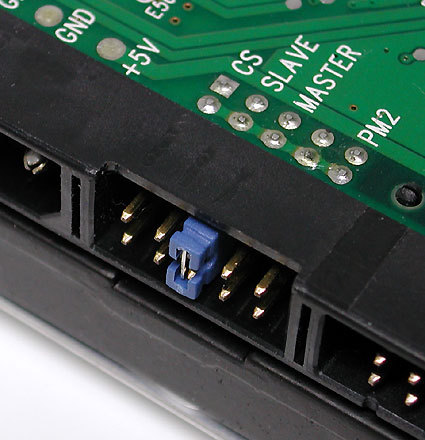
Warning: In most cases, notches in the connector provide protection against reverse insertion or pin alignment/mismatch problems, but older cut-rate cables may lack these features. To prevent mishap, please obey the following rule: the side of the cable that's marked with a colored line (usually red) always attaches to the connector on the motherboard on the side that's labeled with the number 1, both for hard disks and CD/DVD drives (in fact, the stripe denotes the lead associated with pin 1 in the pin block). At the same time, the marked side of the ribbon cable should always be oriented toward the side of the drive where the power cables attach. Also, careful examination of the cable connectors and device or motherboard pin blocks show that both are missing a pin or a hole in the middle of one row. By matching up the missing pin on the drive or motherboard with the missing hole on the ribbon cable connector, correct alignment is always guaranteed.
One ribbon cable can handle two devices, such as a combination of two hard disks or a hard disk and a DVD player or burner. When two devices share a ribbon cable, one must always be configured as the master, and the other as a slave. This configuration usually requires setting a jumper as shown in this picture. A single jumper usually handles this setting on most modern drives; if in doubt about placement, please consult the device documentation (or the vendor's website).
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Glossary
- ATA = Advanced Technology Attachment
- E-IDE = Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics
Current page: ATA/133 (Parallel ATA, UltraDMA/133 Or E-IDE)
Prev Page Inside The Box: Connections Inside A PC System Next Page AGP - Accelerated Graphics Port-
All of the captions are attached to the wrong pictures.Reply
Ugh.
*PLEASE* leave a few blank lines between.