Samsung 1TB 860 QVO SSD Review: QLC Comes To SATA
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
1TB Performance Results
Comparison Products
In today’s performance analysis we're including several popular SATA SSDs. These include the Crucial MX500, Toshiba OCZ TR200, WD Blue 3D, and the 860 QVO’s bigger brother, the Samsung 860 EVO. Additionally, we included the Intel 600p, which is the cheapest QLC-based NVMe SSD on the market (and provides very similar performance to Crucial's QLC P1 SSD). For our real-world tests, we also added results from a 960GB Intel Optane SSD 905P and a 2TB WD Blue HDD for reference between one of the best and slowest storage options in the market.
Trace Testing – PCMark 8 Storage Test 2.0
PCMark 8 is a trace-based benchmark that uses Microsoft Office, Adobe Creative Suite, World of Warcraft, and Battlefield 3 to measure the performance of storage devices in real-world scenarios.
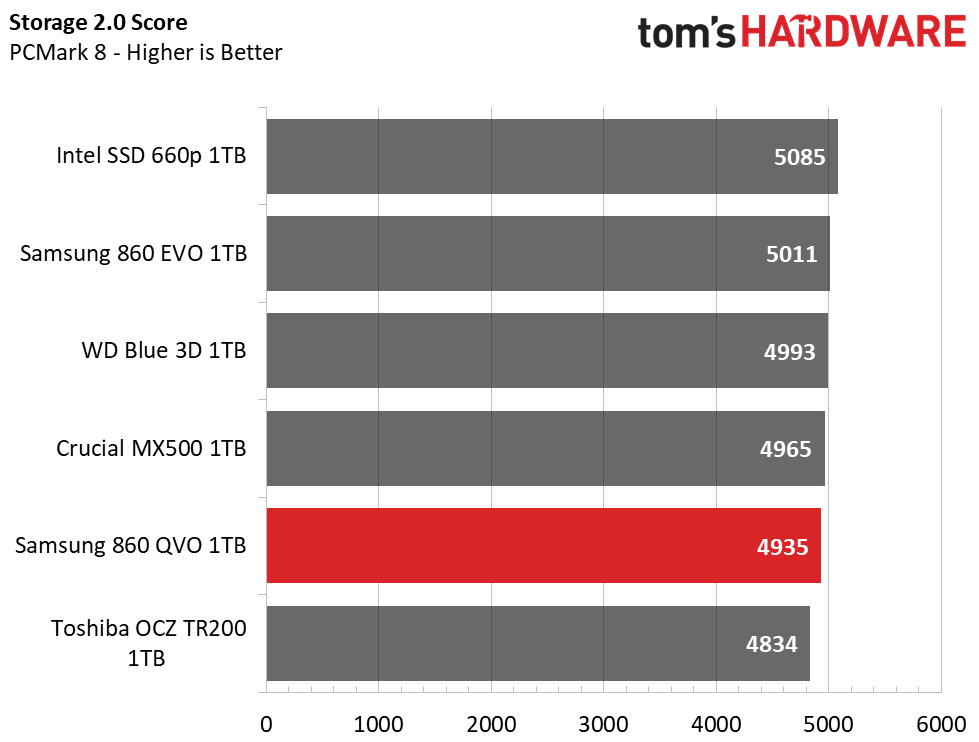
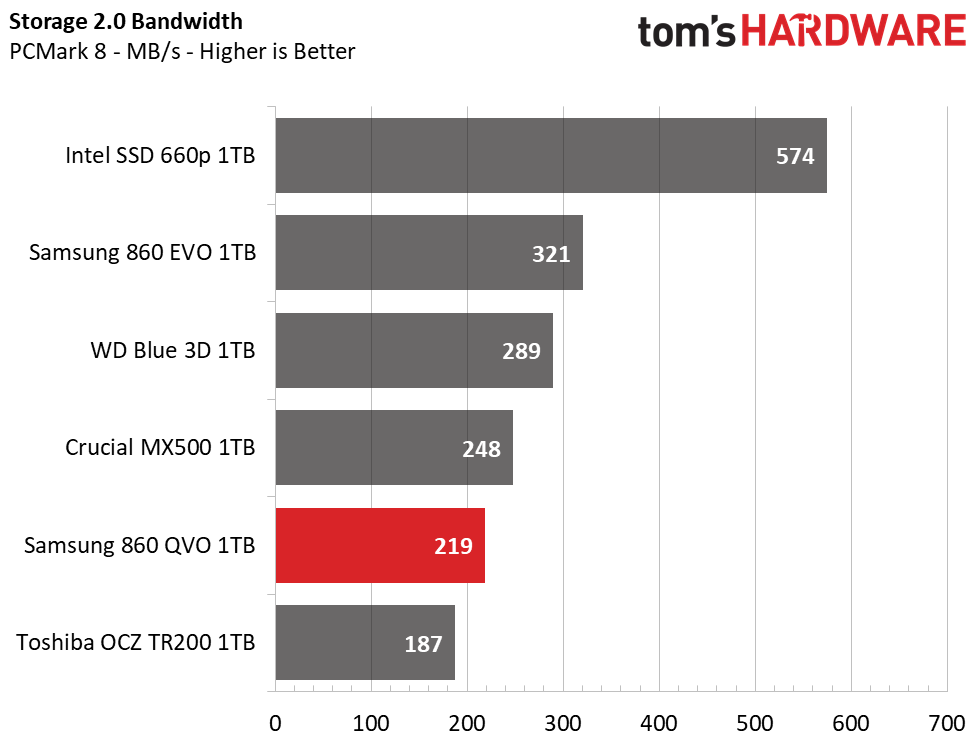
In our first test, Samsung’s 860 QVO ranks 5th overall with an average bandwidth of 219MB/s. This is not as good as the 860 EVO, but it is still a respectable result that outperforms many entry-level TLC SSDs, like the Toshiba OCZ TR200. Meanwhile, the MX500 and WD Blue are faster.
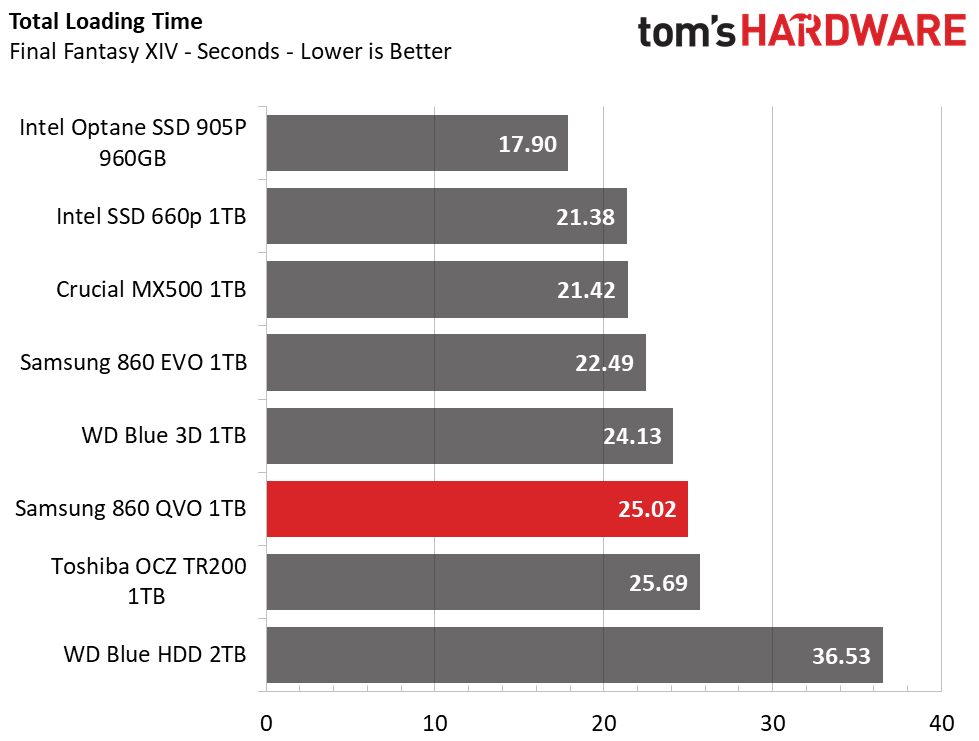
Game Scene Loading - Final Fantasy XIV
The Final Fantasy XIV StormBlood benchmark is a free real-world game benchmark that easily and accurately compares game load times without the inaccuracy of using a stopwatch.
The Samsung 860 QVO ranked near the bottom of the group. The QVO is just two to three seconds slower than the rest of the mainstream competitors, but 11 seconds faster than an HDD.
Transfer Rates – DiskBench
We use the DiskBench storage benchmarking tool to test file transfer performance with our own custom 50GB block of data. Our data set includes 31,227 files of various types, like pictures, PDFs, and videos. We copy the files to a new folder and then follow up with a read test of a newly-written 6 GB file.
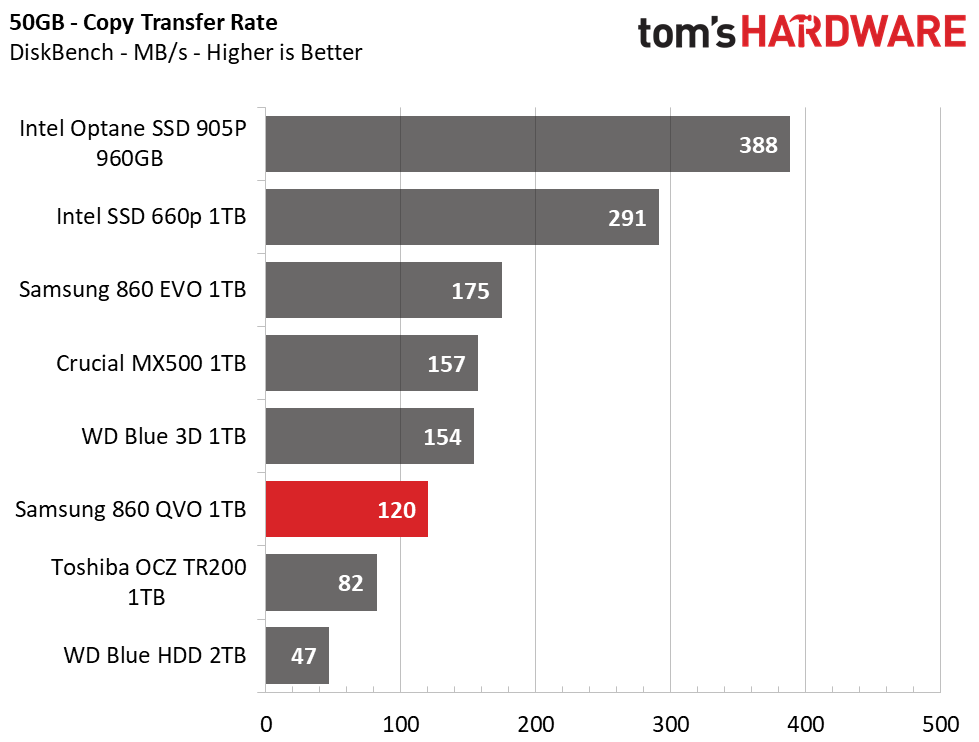
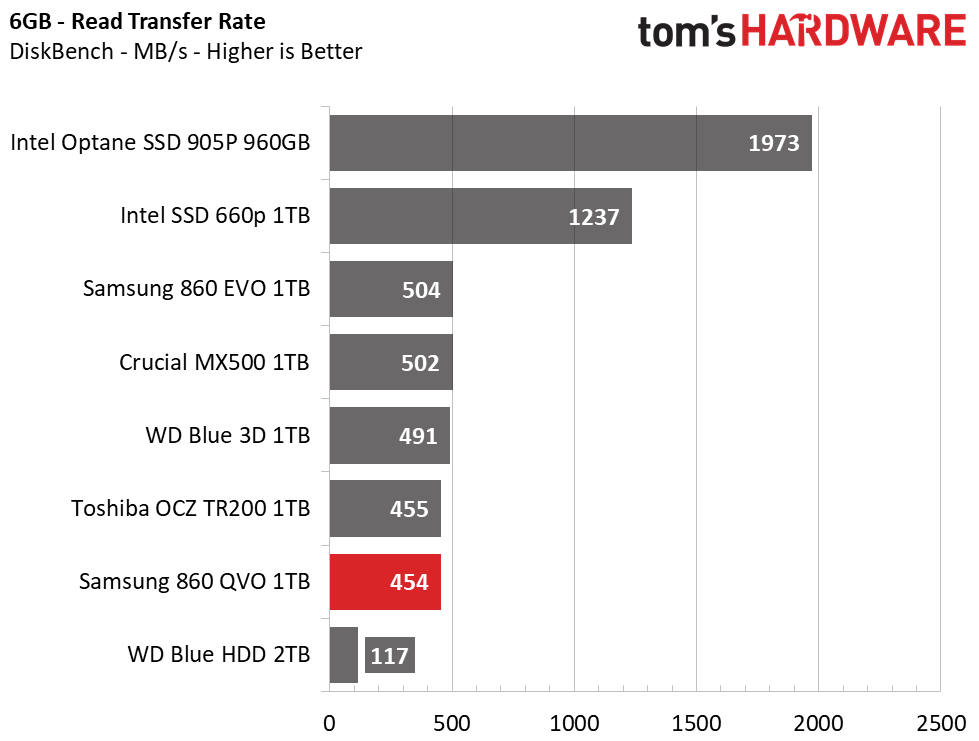
The 860 QVO averaged 120MB/s during our real-world copy test, again landing near the bottom of the pile. It isn’t as fast as the other mainstream TLC SSDs here, but it easily outpaces the hard drive. It averaged 454 MB/s while reading our 6GB file, which is four times faster than the HDD but slightly slower than the rest of the test pool.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
SYSmark 2014 SE
Like PCMark, SYSmark uses real applications to measure system performance. SYSmark takes things much further, however. It utilizes fourteen different applications to run real workloads with real data sets to measure how overall system performance impacts the user experience. BAPCo's SYSmark 2014 SE installs a full suite of applications for its tests, which includes Microsoft Office, Google Chrome, Corel WinZip, several Adobe software applications, and GIMP. That also makes it a great test to measure the amount of time it takes to install widely-used programs after you install a fresh operating system.
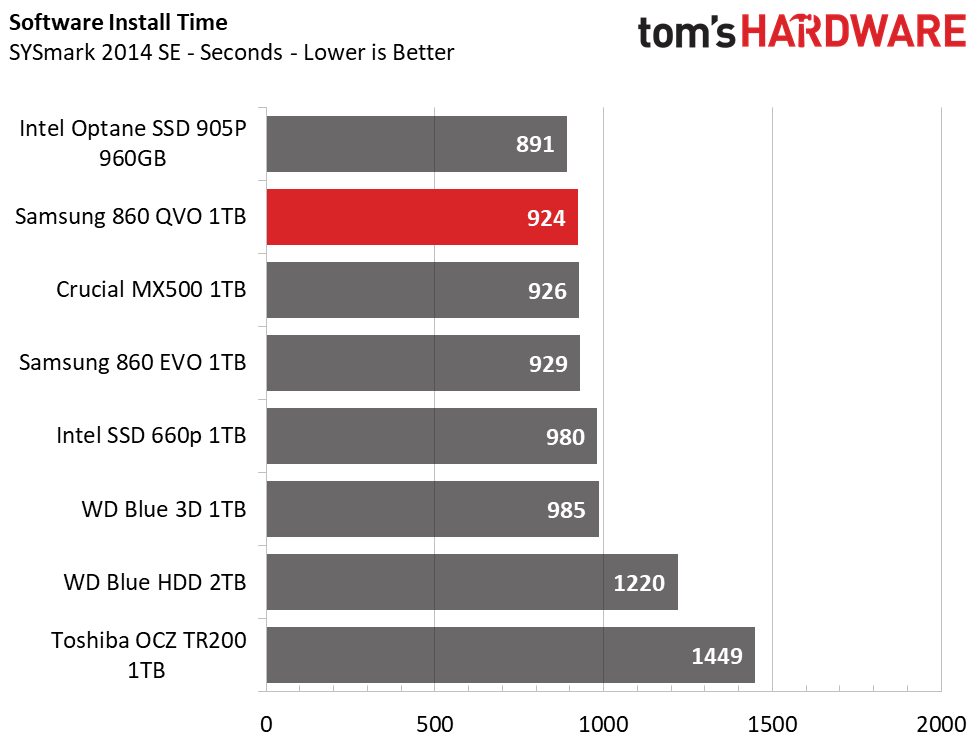
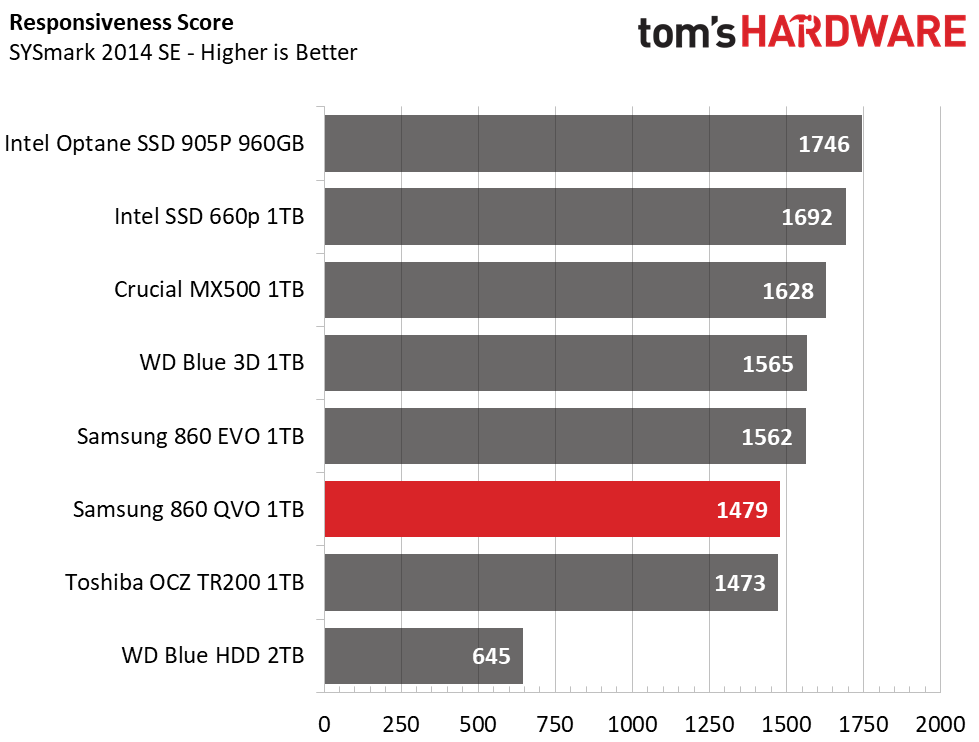
The Samsung 860 QVO installed SYSmark faster than any of the other SSDs. It even challenges Intel's Optane 905p, which is surprising. It looks like the new Intelligent TurboWrite algorithm is effective, but the drive scored just 1479 when we put it through its paces in the full-blown test suite. That's a good score, but it is slightly slower than the rest of the mainstream options.
ATTO
ATTO is a simple and free application that SSD vendors commonly use to assign sequential performance specifications to their products. It also gives us insight into how the device handles different file sizes.
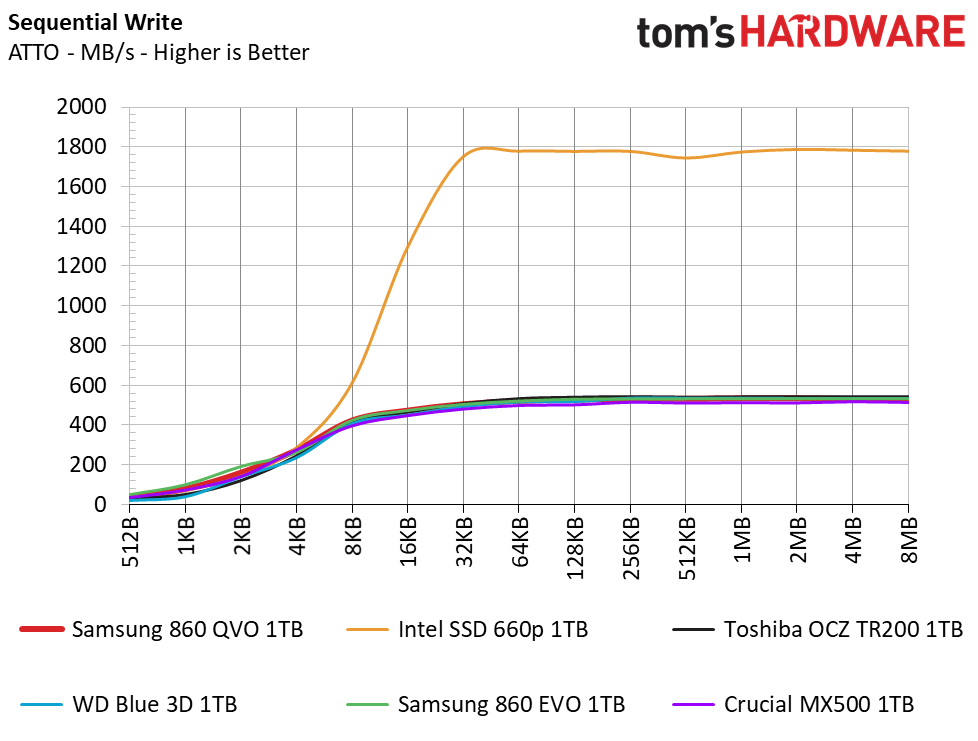
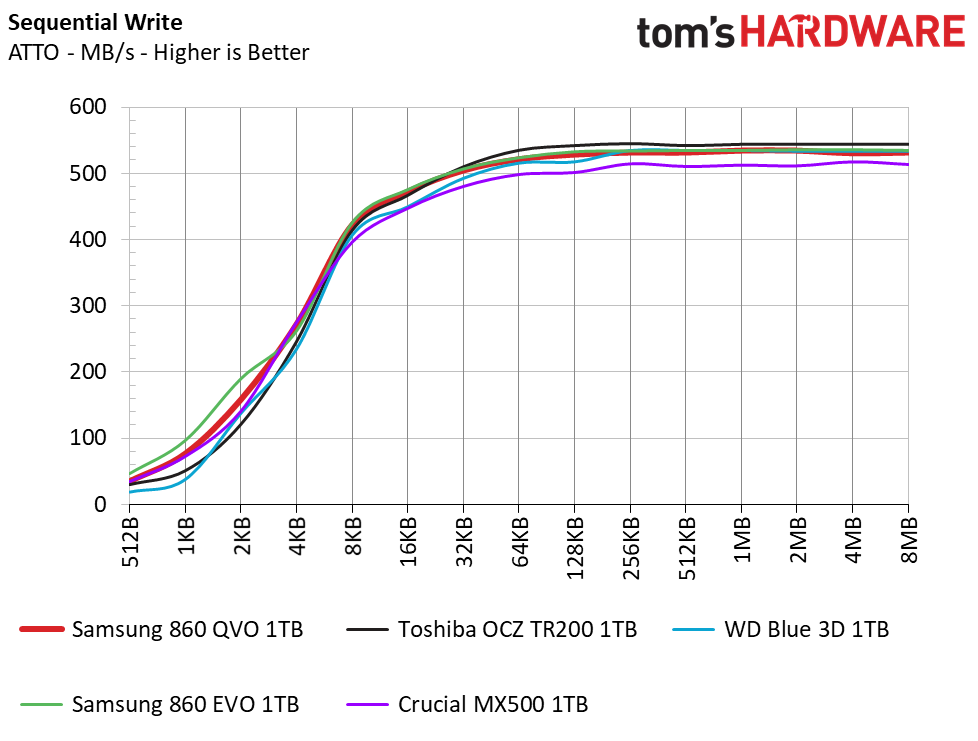
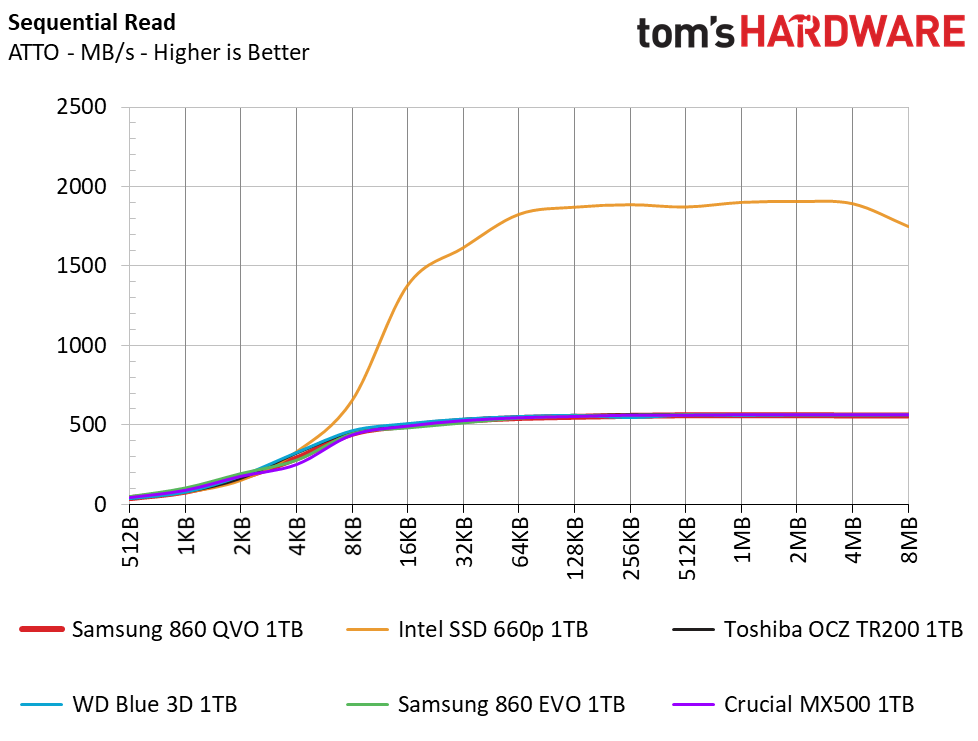
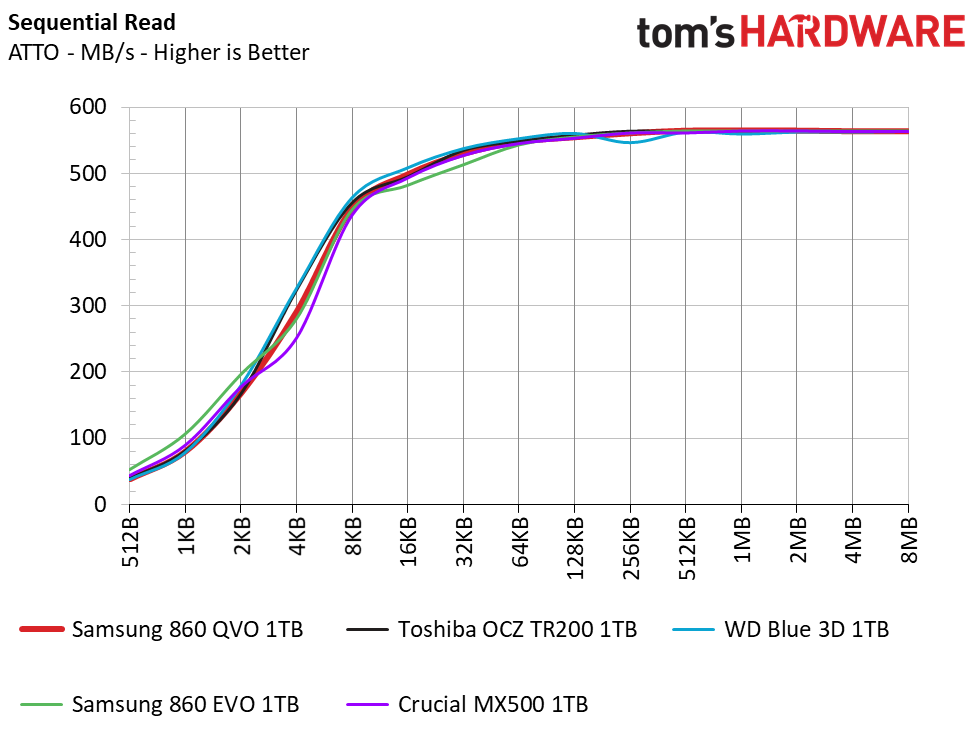
The 860 QVO easily reaches its rated sequential specs of 550/520 MB/s of read/write throughput, which is on par with the rest of our SATA competitors. The Intel 660p towers over the competition with its much faster NVMe interface that allows for speeds of over 1.8 GB/s.
Anvil's Storage Utilities
Anvil's Storage Utility is a commonly-referenced benchmark that simplifies the complex IOMETER benchmark and its underlying Dynamo engine with a one-click software wrapper.
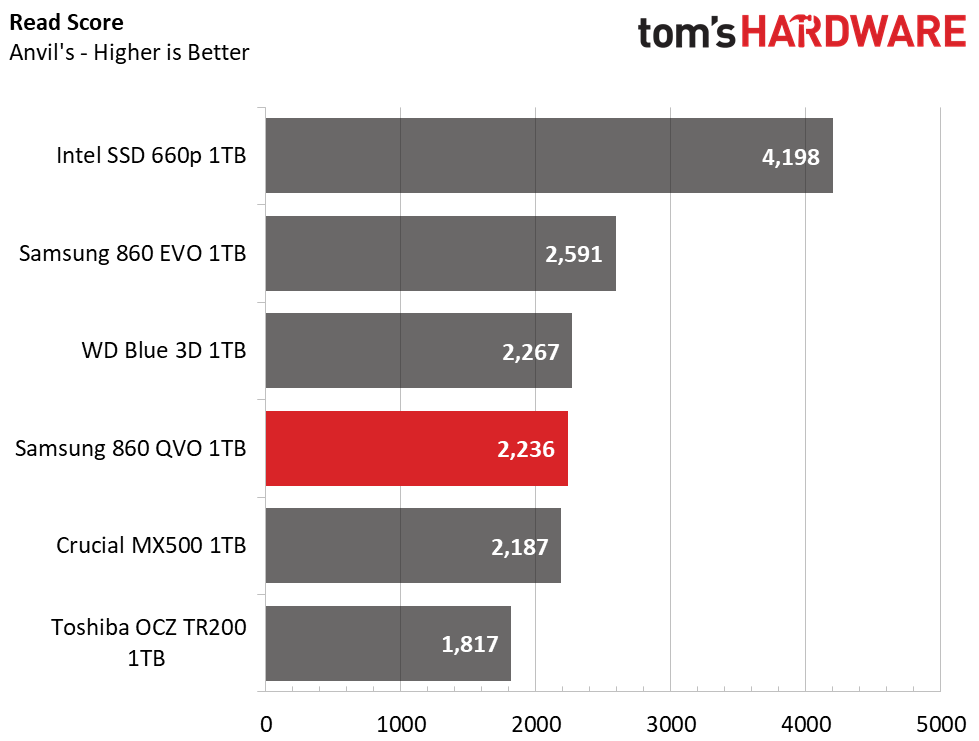
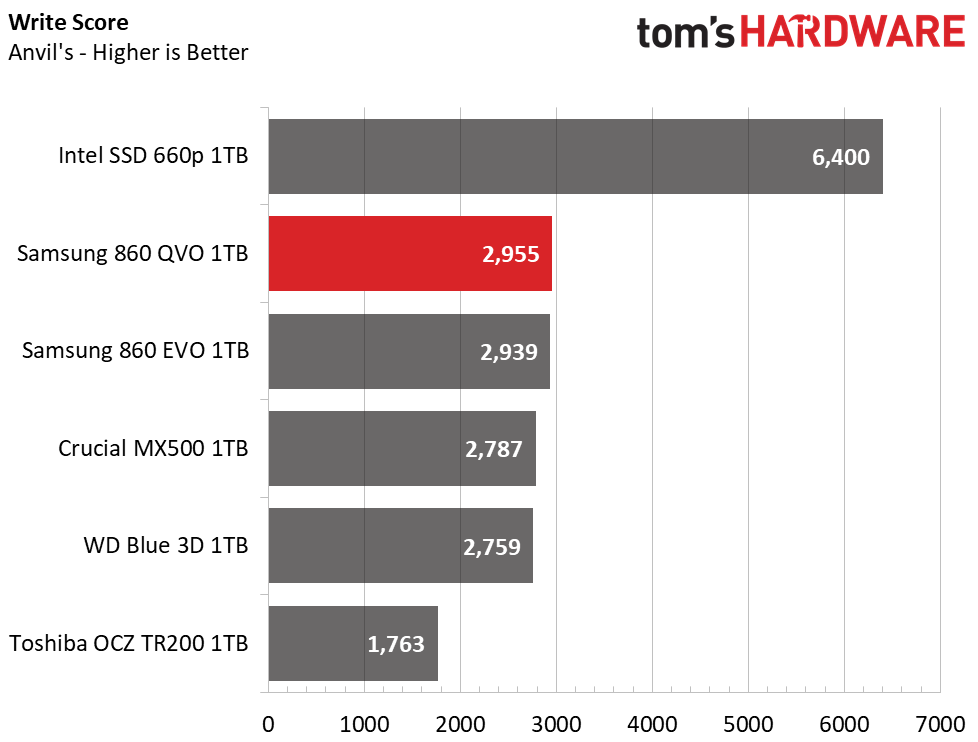
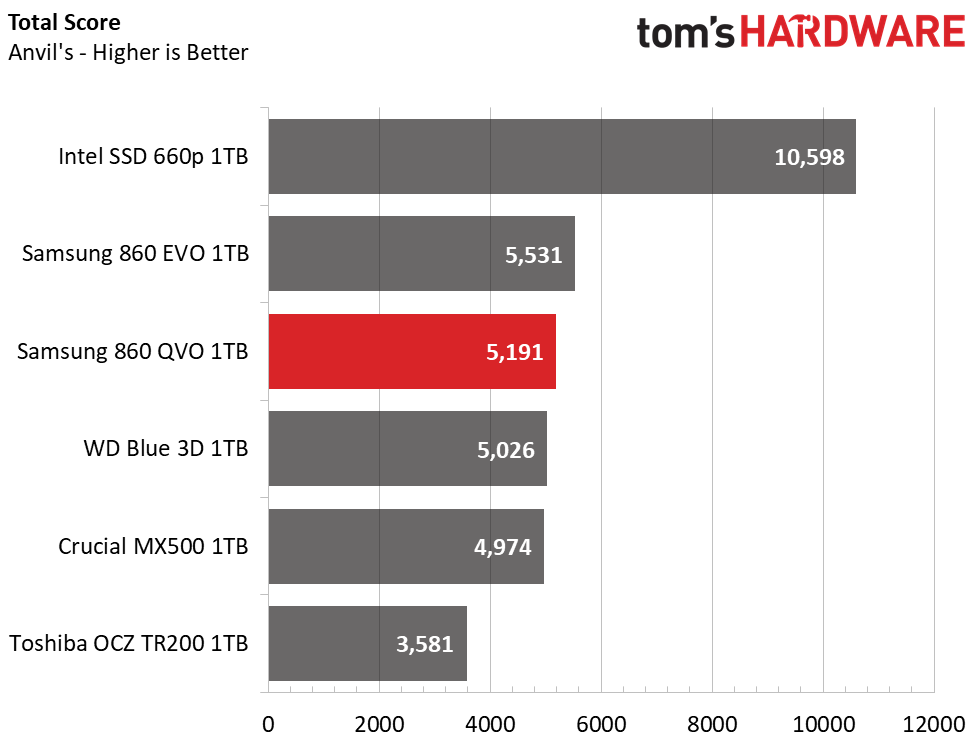
Samsung’s 860 QVO landed just behind the 860 EVO in this benchmark. The drive delivers average read performance, but it surpassed the 860 EVO and all other SATA SSDs during write testing, which helped propel it to third place overall.
CrystalDiskMark
CrystalDiskMark (CDM) is a simple and easy to use file size benchmarking tool.
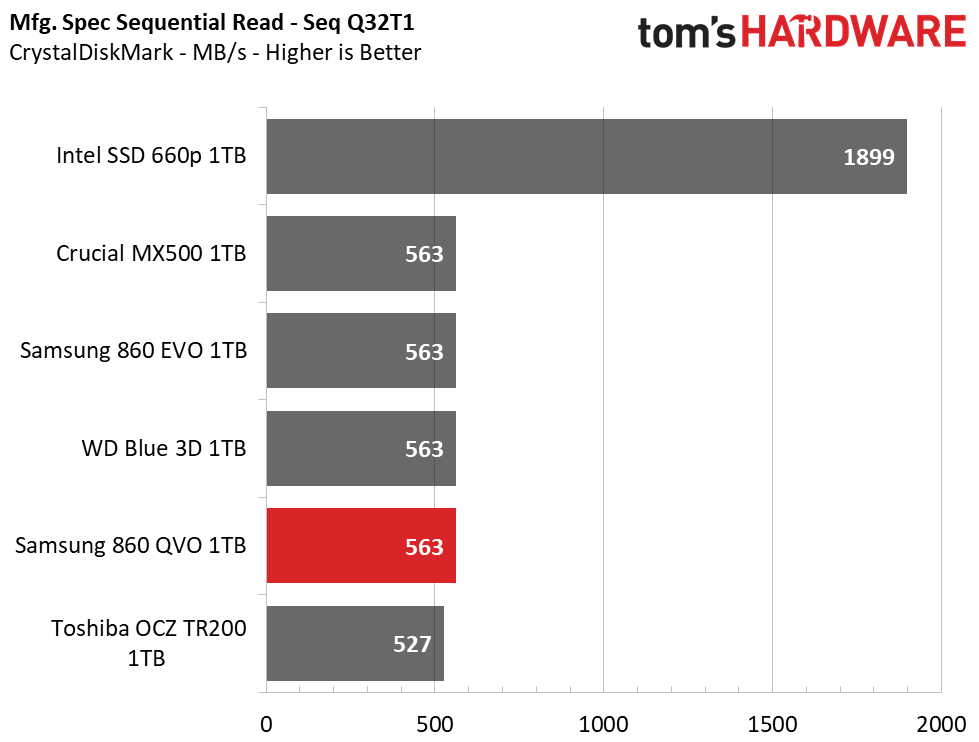
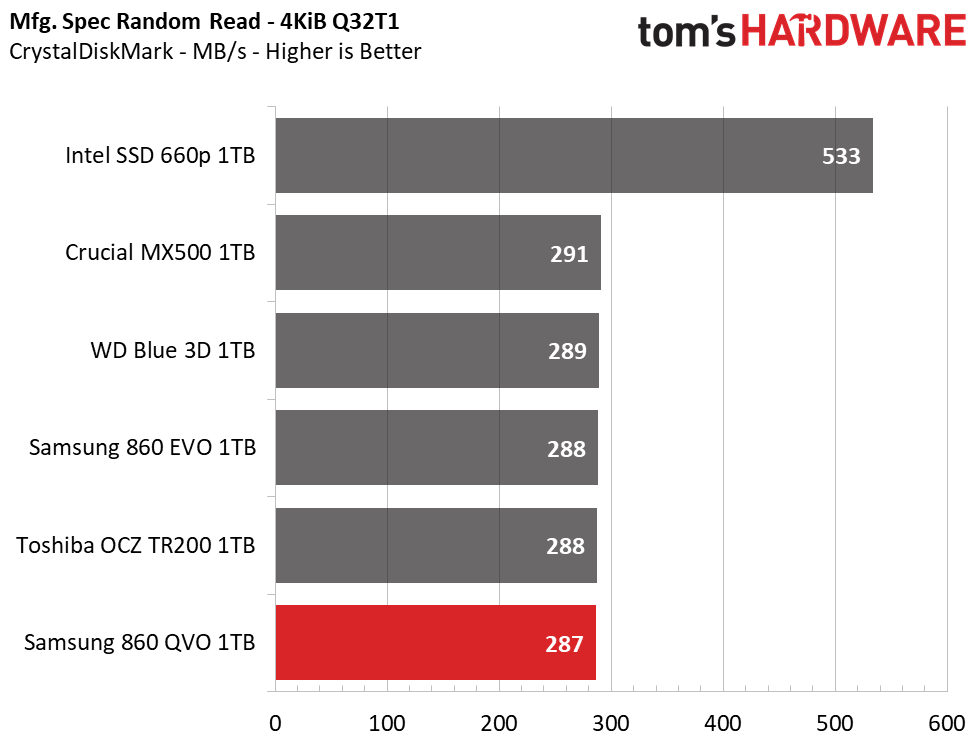
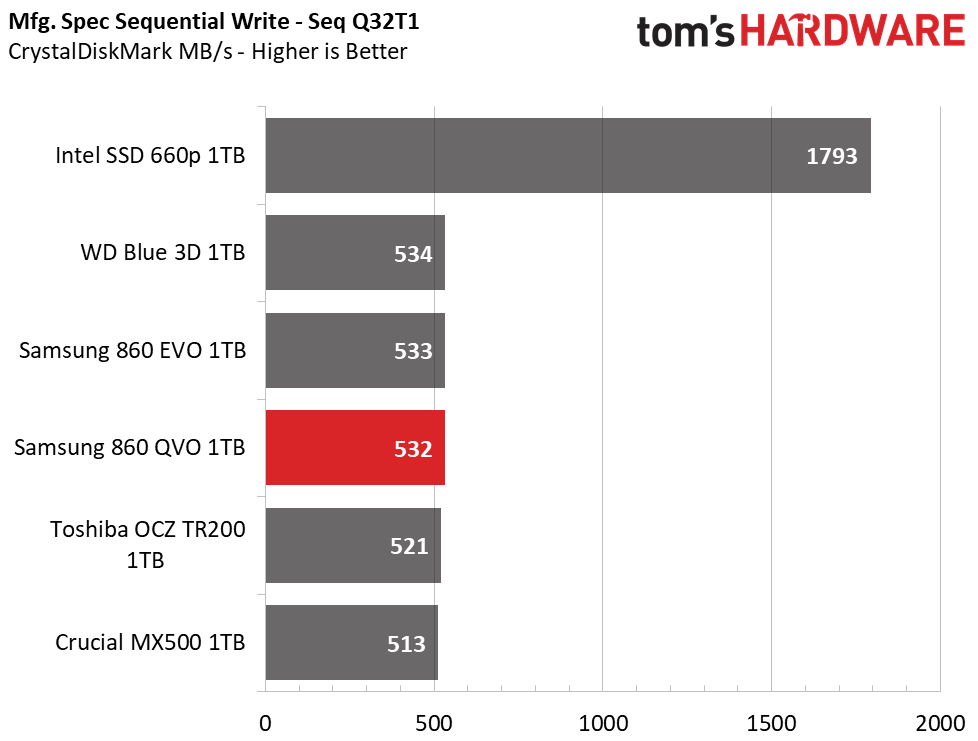
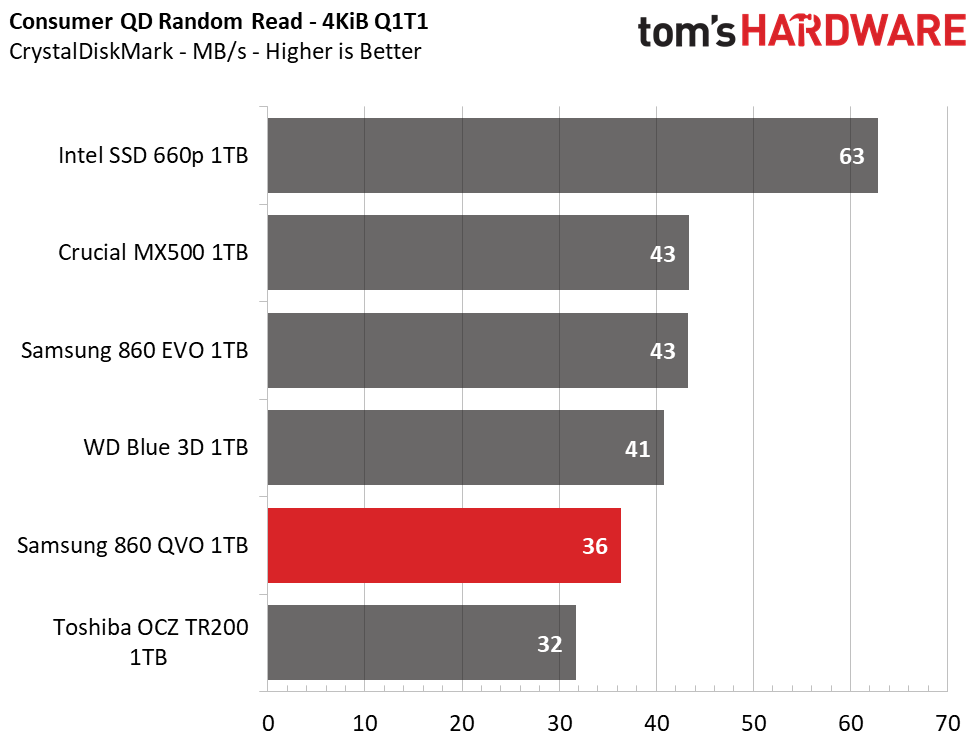
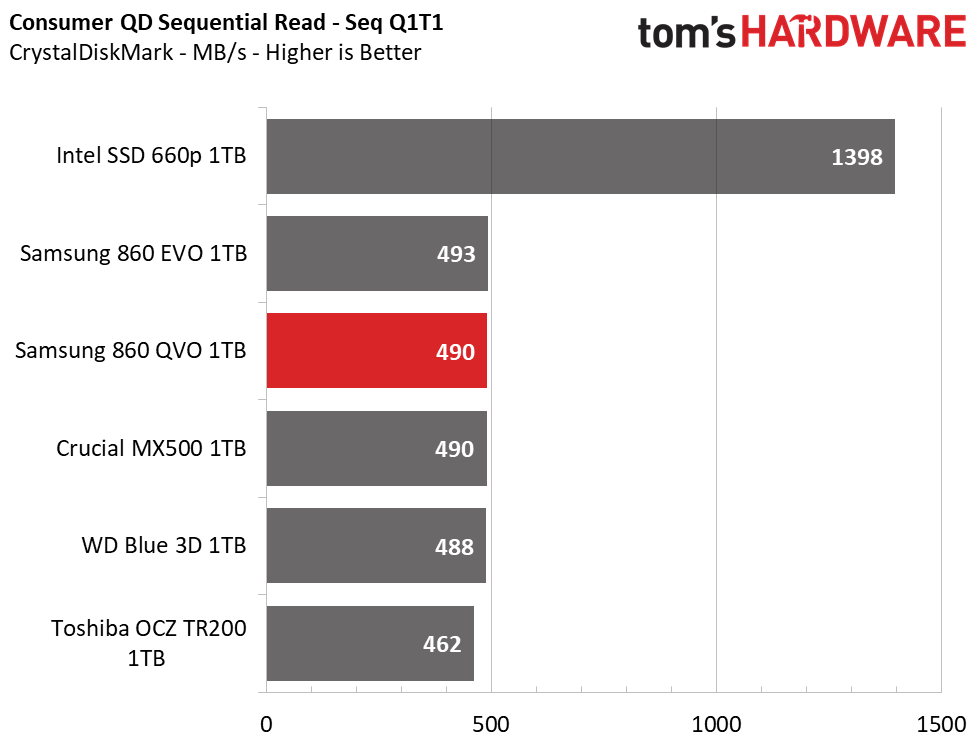
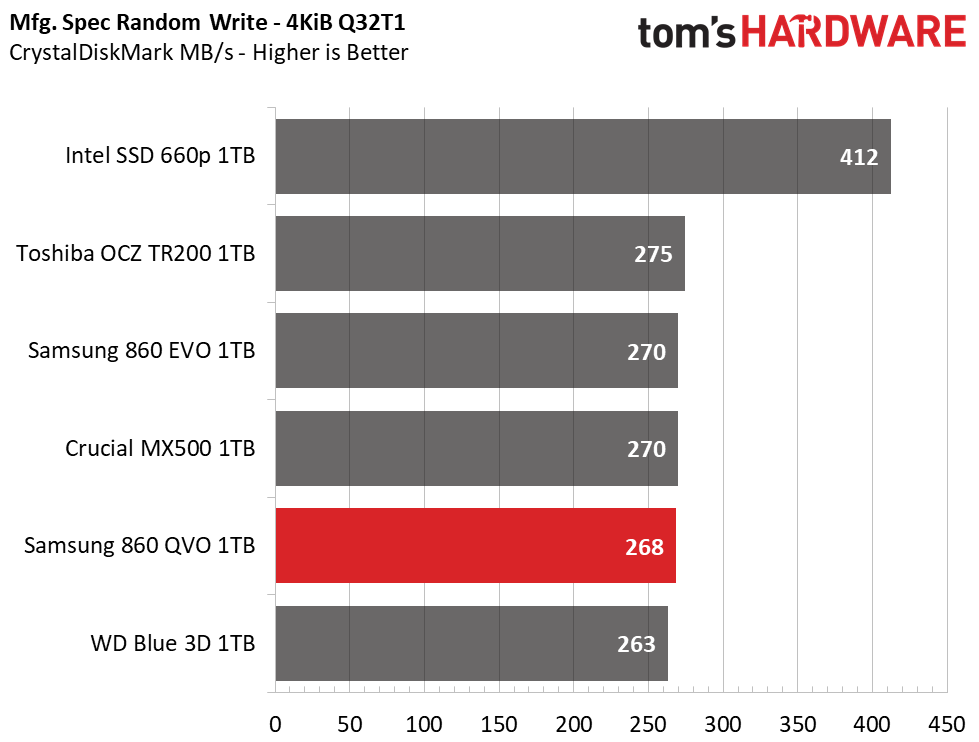
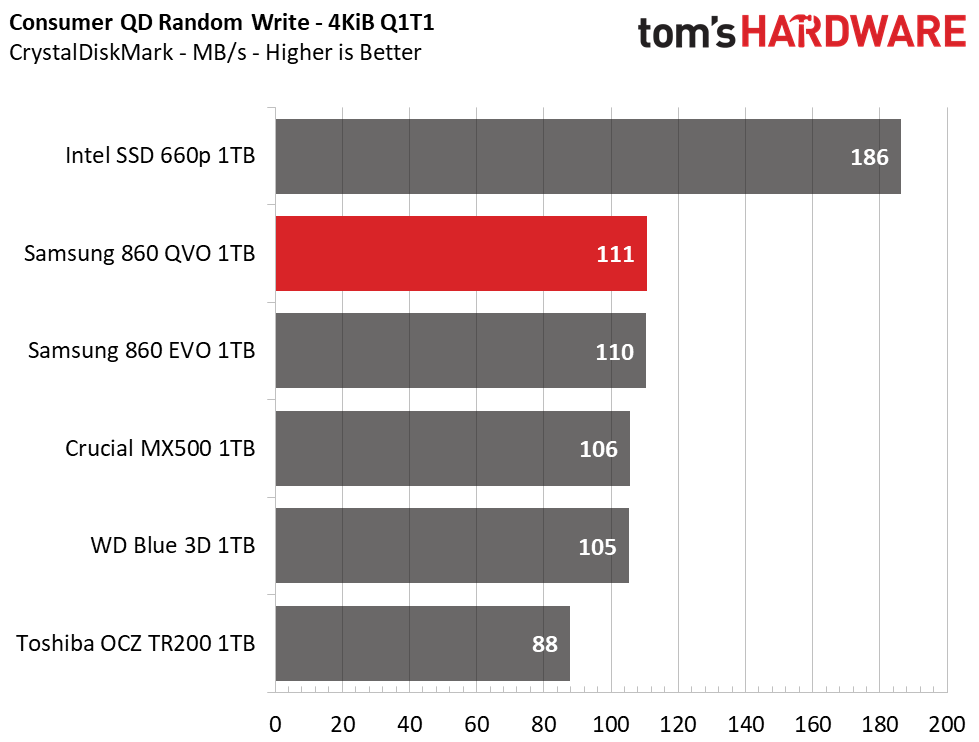
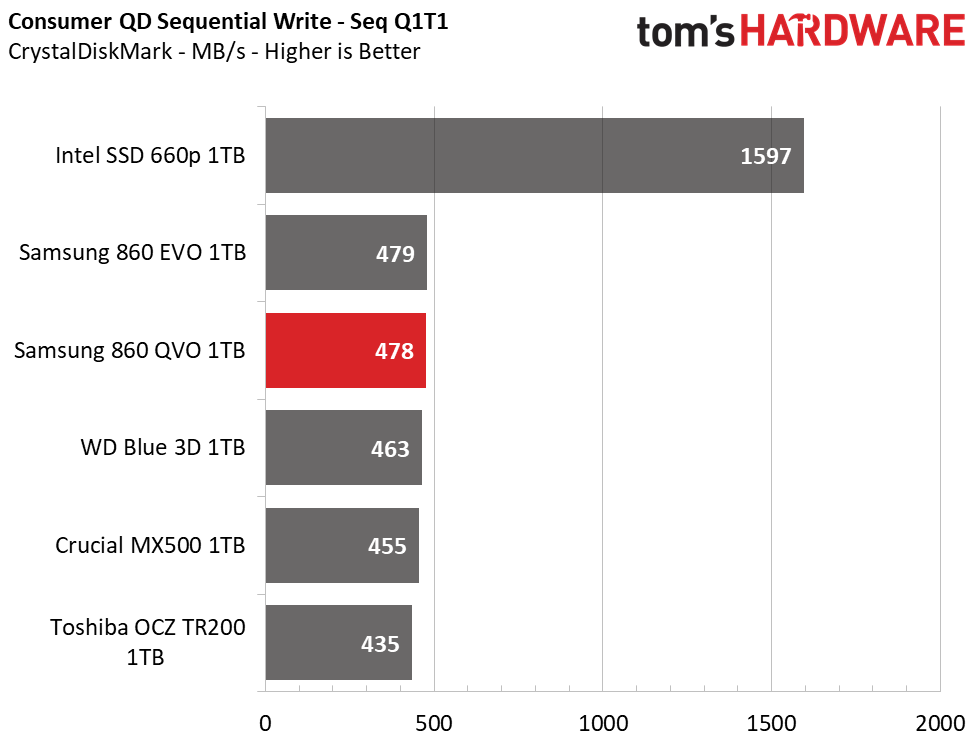
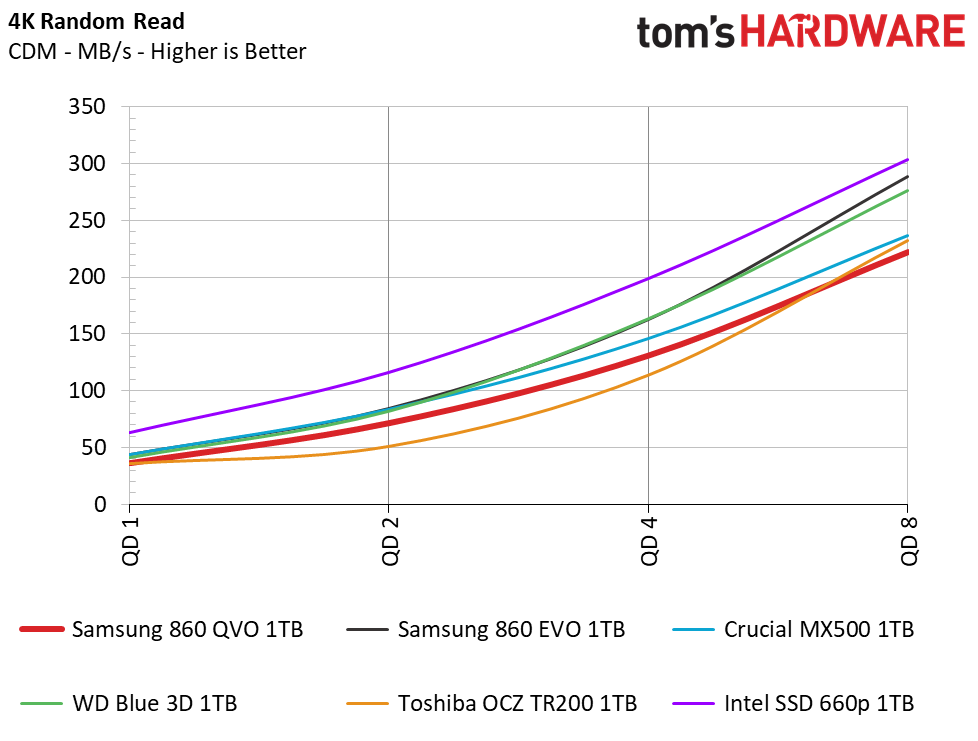
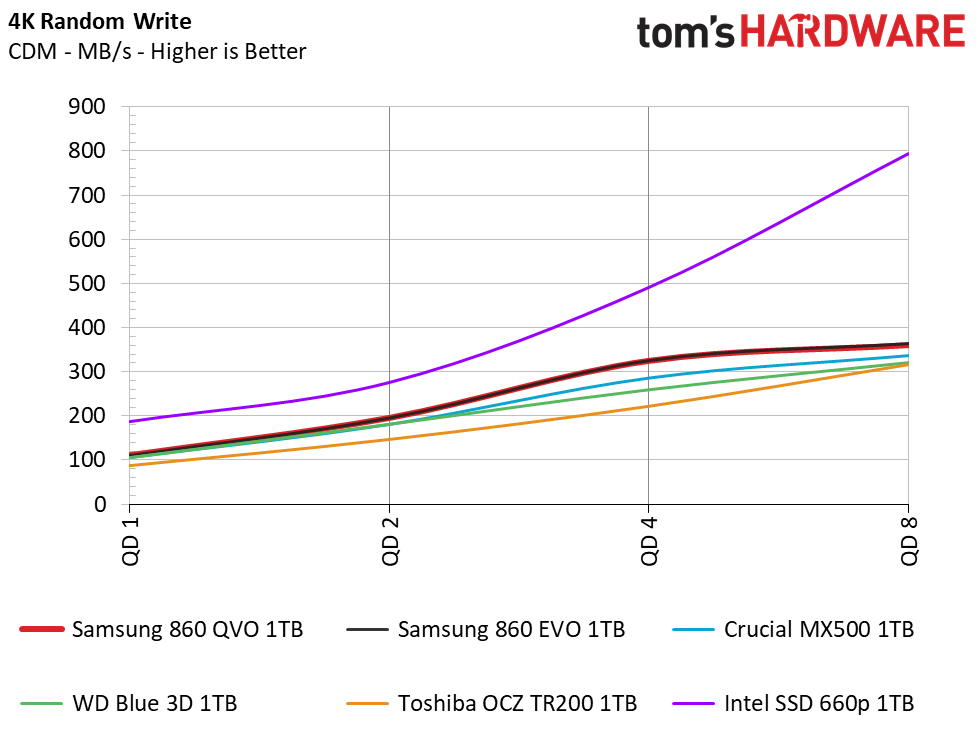
Samsung’s 860 QVO achieved similar performance as the other SSDs in our test pool. We measured peak QD32 (Queue Depth) sequential read/write speeds of 562/532MB/s. The drive also provided similar read and write speeds compared to the 860 EVO at QD1, thus outranking the majority of the test pool.
Sustained Sequential Write Performance
Official write specifications are only part of the performance picture. Most SSD makers implement an SLC cache buffer, which is a fast area of SLC-programmed flash that absorbs incoming data. Sustained write speeds can suffer tremendously once the workload spills outside of the SLC cache and into the "native" TLC or QLC flash. We hammer the SSDs with sequential writes for 15 minutes to measure both the size of the SLC buffer and performance after the buffer is saturated.
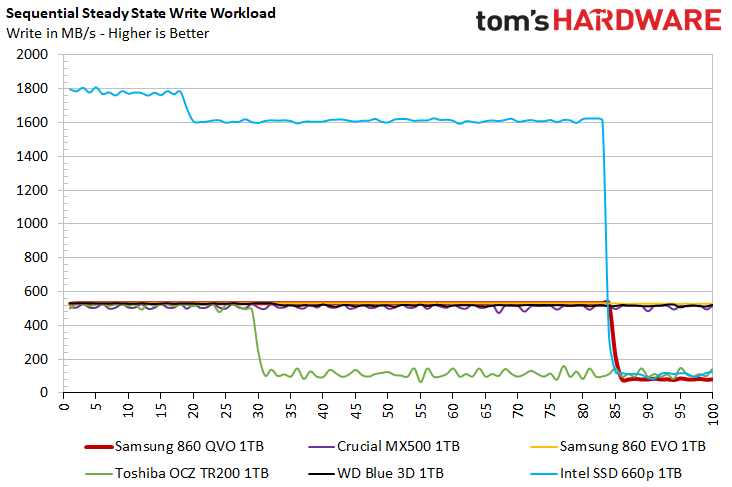
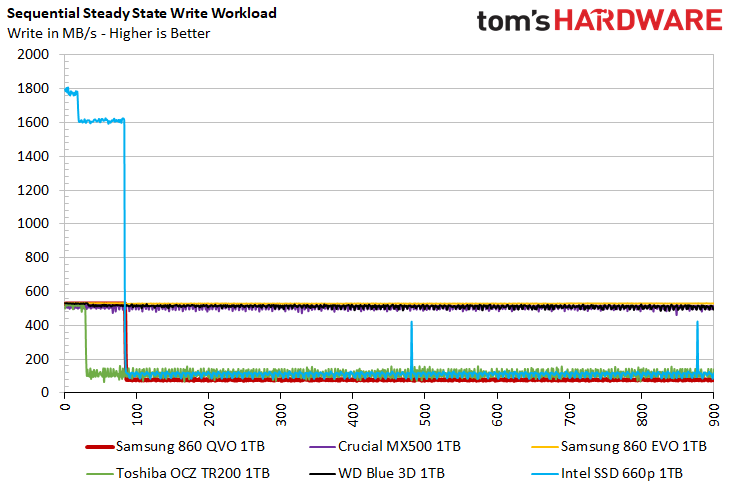
While Intelligent TurboWrite allows for 520MB/s write speeds for up to 42GB of data, performance degrades drastically once the workload fills the buffer. The 860 QVO averages 80MB/s after Intelligent TurboWrite runs out. That's similar to both the TR200 and Intel 660p when the write traffic heads directly to the QLC flash.
Power Consumption
We use the Quarch HD Programmable Power Module to gain a deeper understanding of power characteristics. Idle power consumption is a very important aspect to consider, especially if you're looking for a new drive for your laptop. Some SSDs can consume watts of power at idle while better-suited ones sip just milliwatts. Average workload power consumption and max consumption are two other aspects of power consumption, but performance-per-watt is more important. A drive might consume more power during any given workload, but accomplishing a task faster allows the drive to drop into an idle state faster, which ultimately saves power.
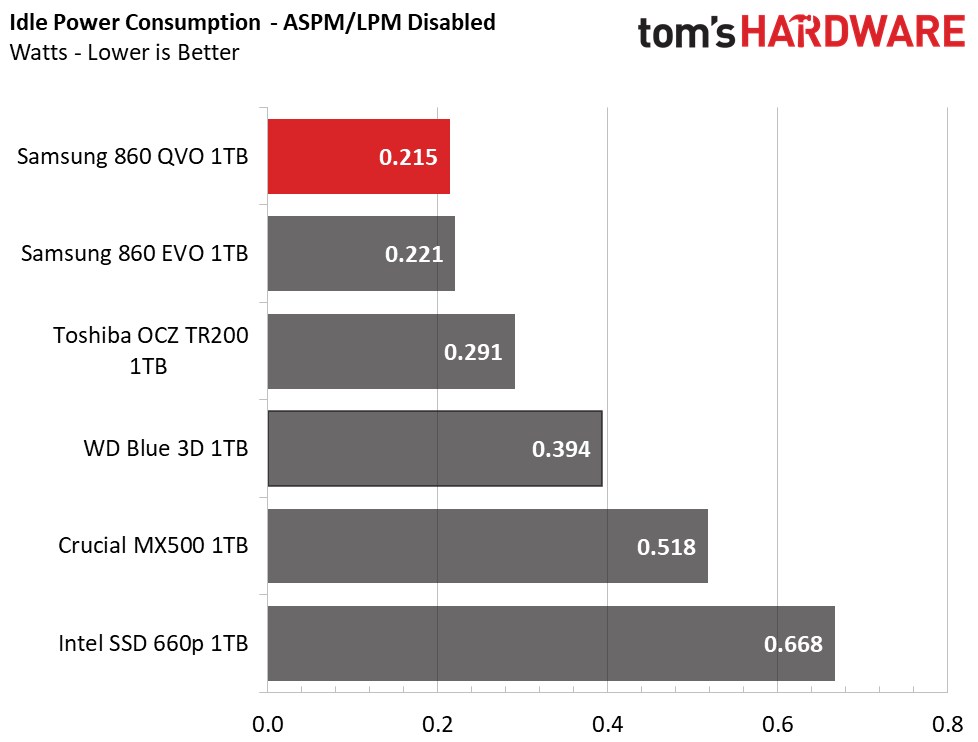
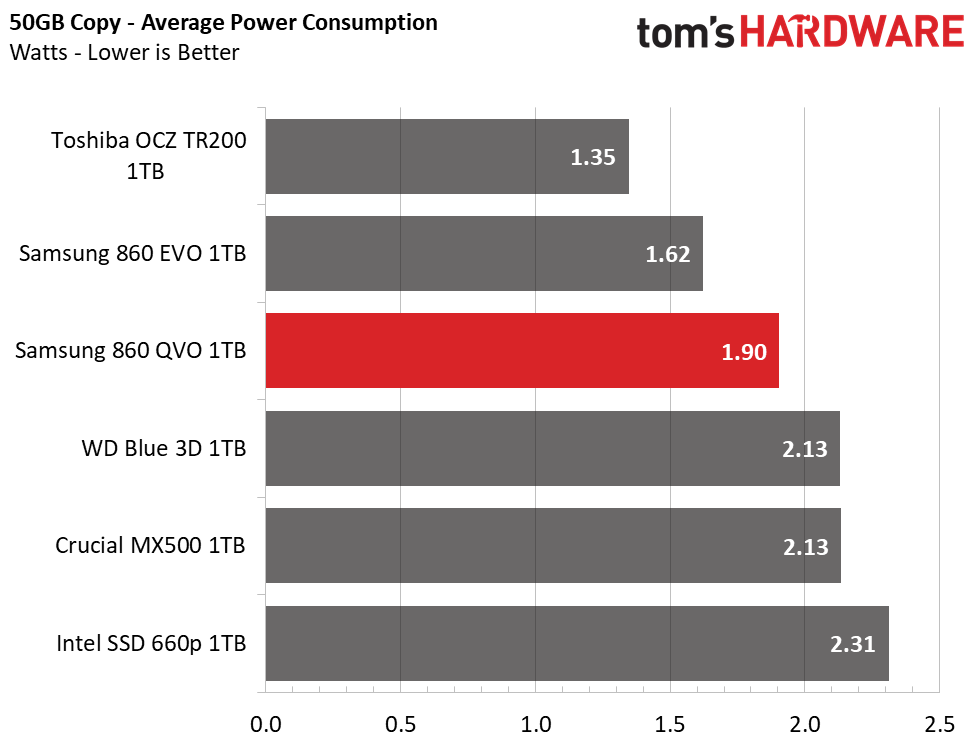
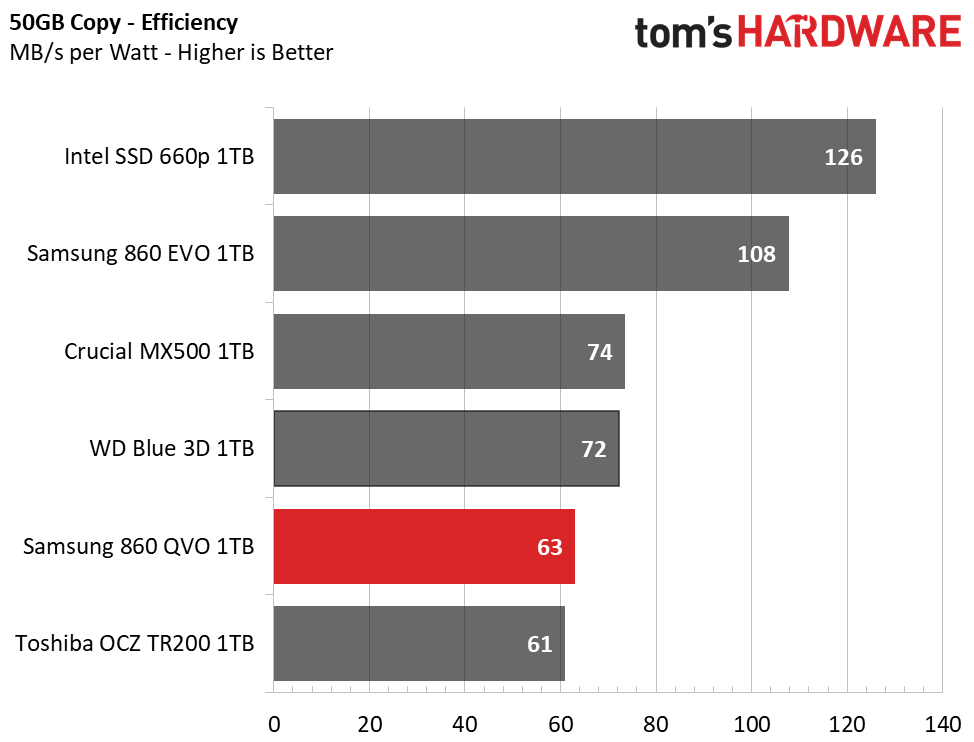
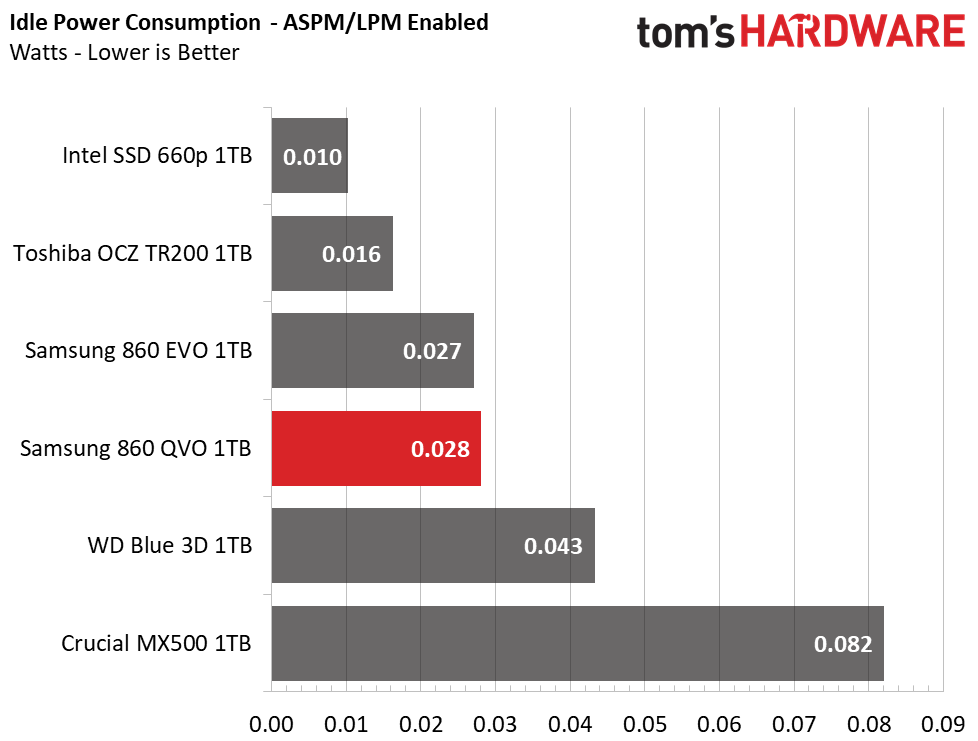
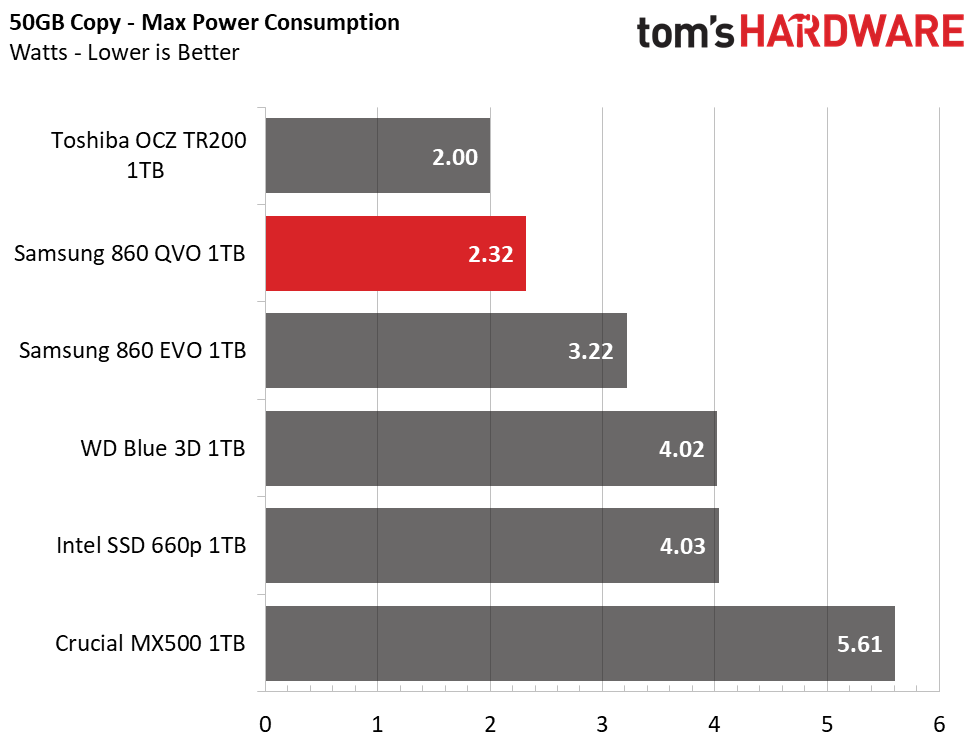
At idle, the 860 QVO consumes the least amount of power in the group when power savings features are disabled. It draws under 30mW with the feature enabled, which is a very good result for a SATA SSD.
The 860 QVO consumes a bit more power than the 860 EVO under load. It averaged 1.9W during our 50GB copy transfer test and hit a maximum of 2.32W. While these numbers are respectable, a lower-than-average transfer rate of 120MB/s resulted in a poor efficiency rating with a score of 63MB/s per watt.
MORE: Best SSDs
MORE: How We Test HDDs And SSDs
MORE: All SSD Content

Sean is a Contributing Editor at Tom’s Hardware US, covering storage hardware.