A 4.1 GHz Dual Core at $130 - Can it be True?
Keeping Cool When Power Consumed Tops 150 Watts at 4.1 GHz, Continued
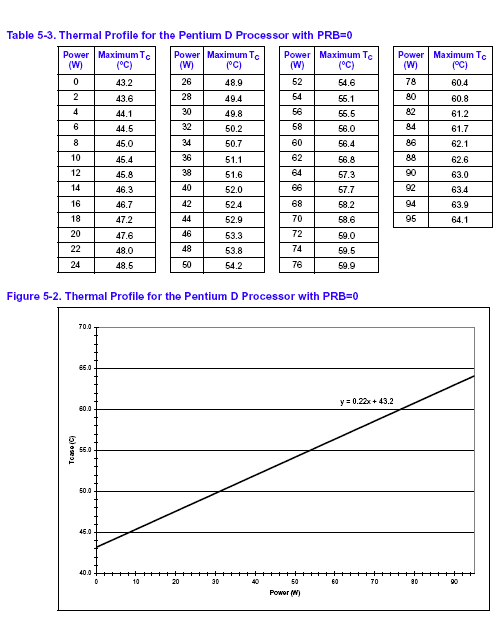
Graphical representation of linear temperature as power consumption increases
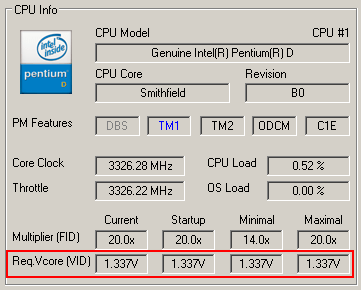
From the same datasheet, you can also observe that this CPU can accept input voltages ranging from 1.2 to 1.4 V. These voltage levels, however, can actually vary within the same series of CPUs; actual values for the CPU in hand are stored in ROM on the chip, and aren't specified on the packaging or in the Spec numbers.
No exact information can be found on the box: only the maximum input voltage of 1.4 V is printed.
The lower the standard voltage of a CPU, the lower its resulting power consumption and cooling requirements.
It's necessary to jump a few hurdles to access the CPU registers and read the actual voltage levels they contain.
A lower CPU voltage level generally indicates a higher-quality CPU. That's because the transistors require less voltage to change states, which also substantially raises the chances of attaining high clock rates.
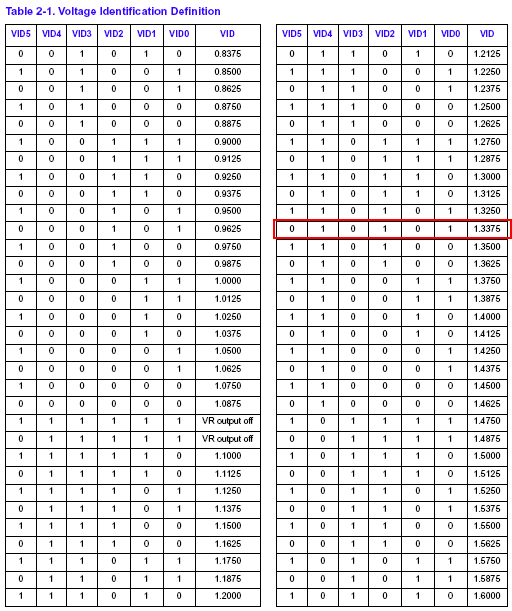
The CPU we purchased for testing shows an internal voltage setting of 1.3375 V.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The voltage level you see on your Pentium D 805 must be the same or lower for you to attain the same overclocking result we achieved or do better.
Current page: Keeping Cool When Power Consumed Tops 150 Watts at 4.1 GHz, Continued
Prev Page Keeping Cool When Power Consumed Tops 150 Watts at 4.1 GHz Next Page Power Consumption Levels Top 200 WTom's Hardware is the leading destination for hardcore computer enthusiasts. We cover everything from processors to 3D printers, single-board computers, SSDs and high-end gaming rigs, empowering readers to make the most of the tech they love, keep up on the latest developments and buy the right gear. Our staff has more than 100 years of combined experience covering news, solving tech problems and reviewing components and systems.
-
Tnias I am quite interested in your post regarding the D 805. Considering that it is now available for around $60.00 (03/20/09), it still sounds like a steal. We just upgraded our Adobe CS2 software to the new CS4 Master Suite, which caused the need for a graphics card upgrade. We have an nVidia GeForce GTX 260, but haven't installed it because our computer is a HP Media Center PCm7350n computers each with a 2.8 GHz CPU on a ASUS P5LP-LE mobo. Your article seemed to imply that there is software available that might adjust the clock from inside windows and we are wondering if it can on that mobo or if we will have to get a different mobo. If so, we are wondering what might be our most cost effective but stable options. We are certainly going to need a new power supply for the GTX 260, which requires 525 Watts. We are looking at just putting in PC Power & Cooling’s, Silencer 610 EPS12V power supplyand letting it go at that, but we are also thinking about upgrading the CPU and mobo if necessary.Reply
Of course, we would like to keep the cost down as much as possible.
We have no idea where the best bang for the buck will be. For us a stable system is more important than blazing speed. Thus, the HP's worked fine for what we originally got them for; it’s just that our graphics and video production software are forcing upgrades in speed and power.
The D850 chip sounds incredible and the power supply we already have to get will handle overclocking that chip. It even sounds like that chip will work in the existing mobo if we can find a way to change the clock speed from inside windows instead of from the BIOS. HP BIOS does not allow adjusting the clock speed in the BIOS but can't BIOS just be changed as well; isn't it just an EPROM?
Anyway, even if we opt for changing out the mobo for another case compatible Asus mobo, we still have to answer the question of which board and chip combination will give us the most stable service for the least cost.
Any ideas that might help us plan the most appropriate upgrade and the least cost? -
amnotanoobie TniasAny ideas that might help us plan the most appropriate upgrade and the least cost?Reply
With the price of components that you need to make this run stable, and the amount of electricity that this would use, a cheap Core 2 and motherboard and DDR2 memory would cost you less in the long run.
Example:
Intel Pentium Dual Core E5200
Kingston DDR2 2x2GB 800MHz
Gigabyte G31M-ES2C
This should cost less than $200.