ATI Graphics Buyer's Guide Spring 2006, Part 1
Gecube Radeon X1900 XTX - Web Support
The Gecube website is available at www.gecube.com, and follows a clear structure, but annoyingly insists on installing a language pack. The driver section is easy to find, and the most recent driver version offered at the time of writing was 8203. Since Gecube obviously does not make any alterations or additions to the reference driver, card owners can also download the most recent version of the Catalyst driver directly from ATI at www.ati.com.
Gecube Radeon X1900 XTX - Overclocking And Heat
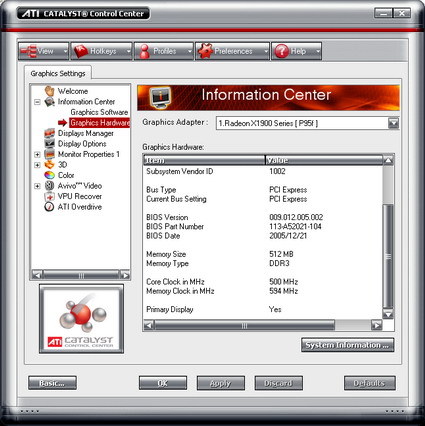
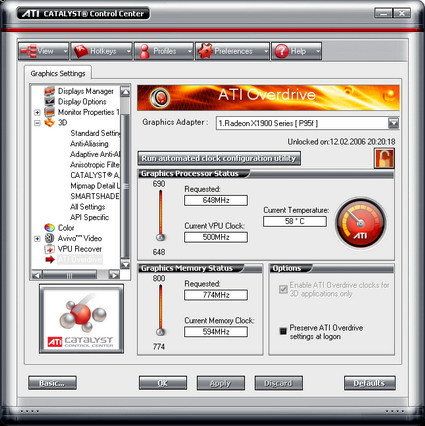
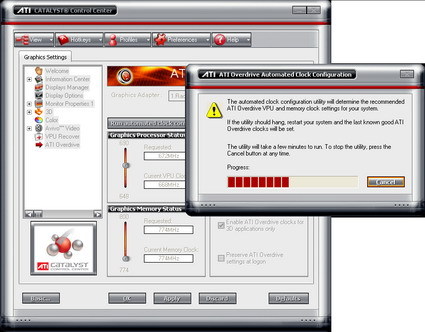
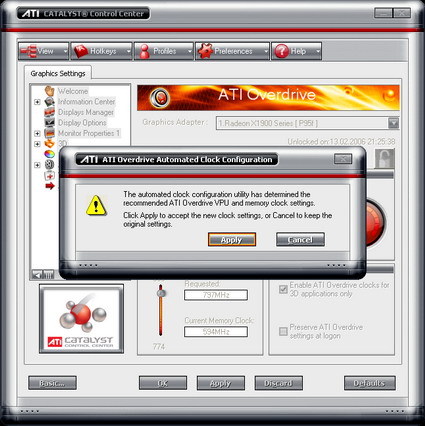
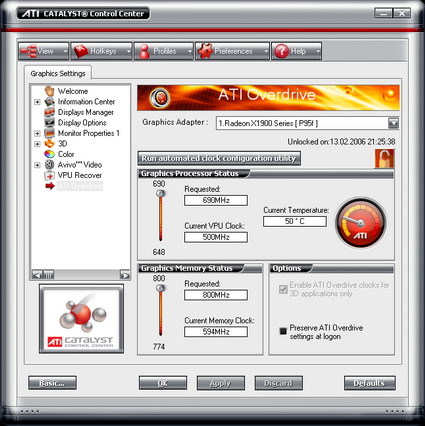
The default clock speeds are given as 500/594 MHz (GPU/memory) in the driver's "information center". The overclocking presets in the overdrive tab of the driver read out as 648/774 MHz. All of our X1900 XTX samples came with this combination of frequencies preset in the overdrive section. In order to overclock the card, the automated clock configuration utility has to be run first, which takes a few minutes. Accepting the speeds suggested by the utility automatically selects them. The Gecube X1900 XTX can be overclocked to a maximum frequency of 690/800 MHz, which increases its overall performance by 2.5 percent. The memory frequency displayed in the screenshot refers to the physical clock speed. Since this is DDR memory, the clock speeds are doubled in the technical specifications.
This chip is a hot piece of hardware indeed. While it idles at a moderate 54°C in 2D mode, it reaches up to 94°C under extended 3D load. The chip seems to cope with the heat quite well, though, but the cooler does its part very noisily.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Gecube Radeon X1900 XTX - Web Support
Prev Page Gecube Radeon X1900 XTX - Tools And Software Next Page HIS Radeon X1600 XT ITurbo IceQ