DDR3-1333 Speed and Latency Shootout
Kingston HyperX PC3-11000
Kingston's HyperX series represents modules that exceed the ratings of standard parts, and its PC3-11000 kit is actually rated for operation at 1375 MHz. The rating is still close enough to the 1333 MHz "standard" data rate for these to be considered "enhanced DDR3-1333," however.
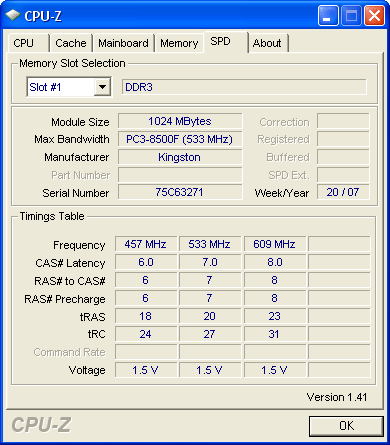
Part number KHX11000D3LLK2/2G provides a dual-channel kit of two 1 GB modules with blue heat spreaders, rated at 7-7-7-20 timing and 1.70 volts. The nonstandard voltage requires manual configuration in BIOS, and the modules default to a slower 533 MHz (DDR3-1066) in order to assure boot capability at a motherboard's default 1.50 volts.
In fact, a DDR3-1333 SPD value isn't even found in the HyperX SPD table, the highest 1.50 volt setting being 609 MHz at CAS 8. Yet, because this RAM defaults to rated timings at a slower clock speed, manual configuration is as easy as changing the speed and voltage in motherboard BIOS.
A 457 MHz SPD value is also able to be automatically configured for DDR3-800 operation when FSB-800 processors are used, while the 533 MHz DDR3-1066 value works for FSB-1066, FSB-1333 and FSB-1600 processors.
Current page: Kingston HyperX PC3-11000
Prev Page Kingston ValueRAM PC3-10600 Next Page Mushkin Enhanced EM3-10666Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
-
dv8silencer I have a question: on your page 3 where you discuss the memory myth you do some calculations:Reply
"Because cycle time is the inverse of clock speed (1/2 of DDR data rates), the DDR-333 reference clock cycled every six nanoseconds, DDR2-667 every three nanoseconds and DDR3-1333 every 1.5 nanoseconds. Latency is measured in clock cycles, and two 6ns cycles occur in the same time as four 3ns cycles or eight 1.5ns cycles. If you still have your doubts, do the math!"
Based off of the cycle-based latencies of the DDR-333 (CAS 2), DDR2-667 (CAS 4), and DDR3-1333 (CAS8), and their frequences, you come to the conclusion that each of the memory types will retrieve memory in the same amount of time. The higher CAS's are offset by the frequences of the higher technologies so that even though the DDR2 and DDR3 take more cycles, they also go through more cycles per unit time than DDR. How is it then, that DDR2 and DDR3 technologies are "better" and provide more bandwidth if they provide data in the same amount of time? I do not know much about the technical details of how RAM works, and I have always had this question in mind.
Thanks -
Latency = How fast you can get to the "goodies"Reply
Bandwidth = Rate at which you can get the "goodies" -
So, I have OCZ memory I can run stable atReply
7-7-6-24-2t at 1333Mhz or
9-9-9-24-2t at 1600Mhz
This is FSB at 1600Mhz unlinked. Is there a method to calculate the best setting without running hours of benchmarks? -
Sorry dude but you are underestimating the ReapearX modules,Reply
however hard I want to see what temperatures were other modules at
a voltage of ~ 2.1v, does not mean that the platinum series is not performant but I saw a ReapearX which tended easy to 1.9v(EVP)940Mhz, that means nearly a DDR 1900, which is something, but in chapter of stability/temperature in hours of functioning, ReapearX beats them all. -
All SDRAM (including DDR variants) works more or less the same, they are divided in banks, banks are divided in rows, and rows contain the data (as columns).Reply
First you issue a command to open a row (this is your latency), then in a row you can access any data you want at the rate of 1 datum per cycle with latency depending on pipelining.
So for instance if you want to read 1 datum at address 0 it will take your CAS lat + 1 cycle.
So for instance if you want to read 8 datums at address 0 it will take your CAS lat + 8 cycle.
Since CPUs like to fill their cache lines with the next data that will probably be accessed they always read more than what you wanted anyway, so the extra throughput provided by higher clock speed helps.
But if the CPU stalls waiting for RAM it is the latency that matters.