Seven of NVIDIA's Latest and Greatest Cards Tested
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
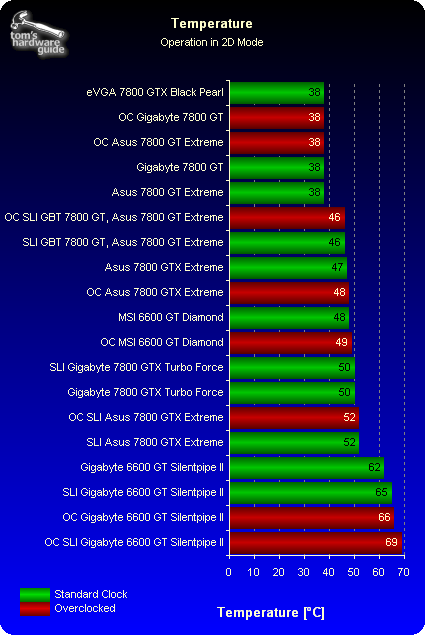
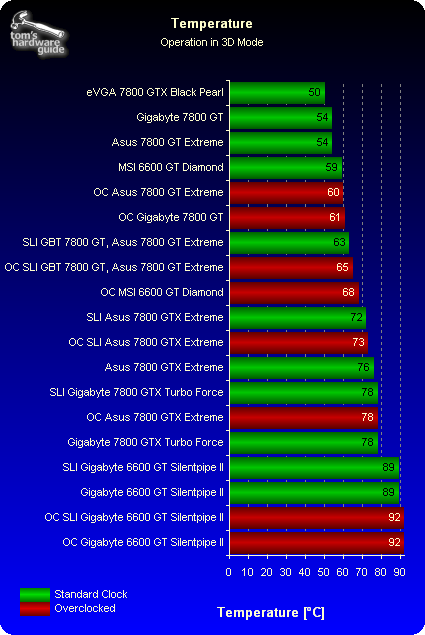
Heat
The temperature of the GPU can be monitored directly through the NVIDIA drivers. One side effect of overclocking is that it always produces higher core temperatures. The water-cooled eVGA card has no trouble keeping cool even at 600/1800 MHz, staying at a moderate 50° C. While the conventional air coolers of its competitors are loud, they also deal with the heat quite well. In contrast, the passively cooled Asus 6600 GT Silentpipe-II gets extremely hot. Overclocking only aggravates the situation further, and users should ensure a good airflow in their cases.
Users planning to use the Coolbits registry hack to overclock their cards should factor in higher GPU temperatures. In other words, we recommend the following procedure to prevent damaging the hardware through overheating. First, heat up the card by putting it under heavy 3D load. Then switch to the unlocked driver as quickly as possible, and run the automatic frequency detection tool. The suggested frequency will be much lower than what would be attainable with a cooler card, and this will help you avoid overheating the unit with excessive clock speeds.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.