Display Power Consumption: CRTs Versus TFT-LCDs
An increasing number of flat panel displays are based on LED backlighting, and their manufacturers aren't shy about promoting the technology's benefits to power consumption. We checked the claims to see if the promised savings are worth emphasizing.
Benchmark Results: Different Brightness Testing
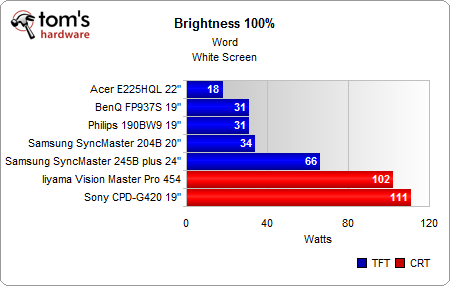
Running at 100% brightness represents a worst-case scenario for power consumption. The results match our test with Microsoft Word and a blank page.
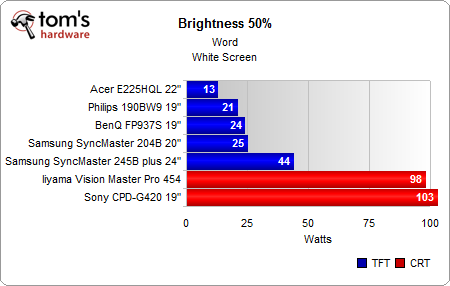
Switching brightness to 50% makes a significant difference, as the displays reduce their power consumption as follows:
- Acer 22”: 18 W to 13 W (-28%)
- Philips 19”: 31 W to 21 W (-32%)
- BenQ 19”: 32 W to 24 W (-25%)
- Samsung 20”: 34 W to 25 W (-26%)
- Samsung 24”: 66 W to 44 W (-33%)
- Iiyama 19” CRT: 102 W to 98 W (-4%)
- Sony 19” CRT: 111 to 103 W (-7%)
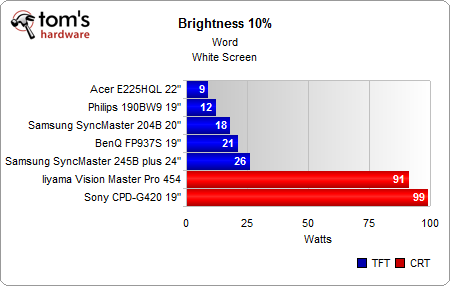
Finally, the reduction to only 10% display brightness dramatically reduces power consumption with a white screen to as little as 9 W on the 22” Acer display, 12 to 21 W on the 19”/20” displays, and 26 W on the 24” Samsung. The only monitors showing little impact are the CRTs.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Benchmark Results: Different Brightness Testing
Prev Page Benchmark Results: Movie Playback And Windows Screens Next Page Conclusion