Changing Of The Guard: 2.5” Hard Drives In The Enterprise
Benchmark Results: Temperature, Power, And Efficiency
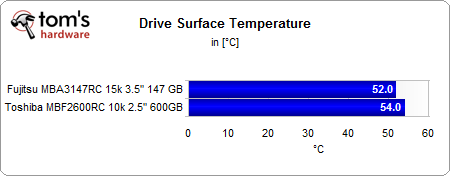
Drive surface temperatures don't differ much, as the 3.5” drive can dissipate its heat across a much larger surface.
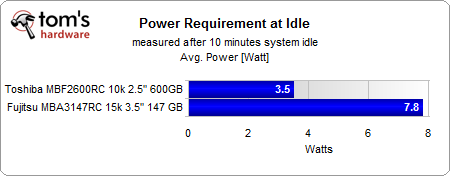
Having 3.5W idle draw compared to 7.8W is significant.
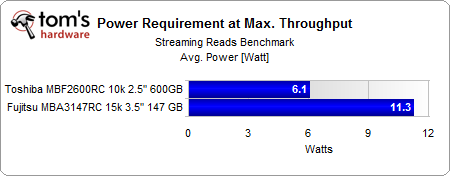
Similarly, 6.1W versus 11.3W at peak throughput obviously favors the 2.5” drive.
Toshiba's 2.5” MBF2600RC power draw under a constant, limited load looks remarkably close to idle power. The 15,000 RPM, 3.5” Fujitsu MBA3147RC looks closer to peak power in this workload.
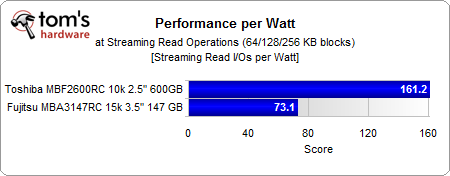
Want efficiency? The 2.5” drive provides more than twice the throughput performance per watt than the 3.5” high speed model.
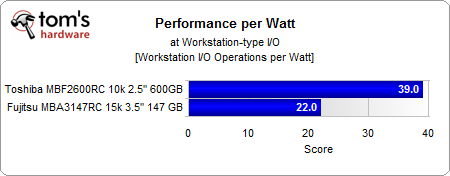
Efficiency during I/O operations does not differ as significantly, but the result still almost doubled Toshiba's 2.5” drive.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Benchmark Results: Temperature, Power, And Efficiency
Prev Page Benchmark Results: PCMark Application Performance Next Page Conclusion