External Battery Roundup: Stay Away From The Wall Socket
External Batteries: How Do They Work?
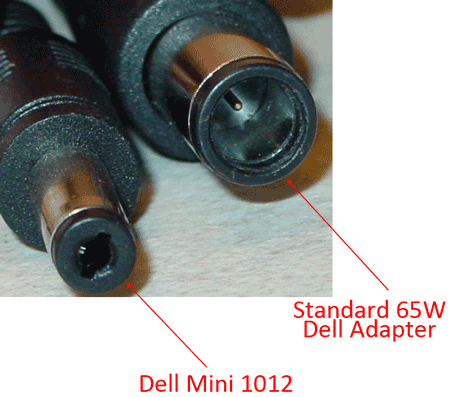
Extended batteries are unlike the battery that ships with your notebook. The most obvious difference is that they come with a variety of tips, since they claim universality with each manufacturer's specific power connector.
Even within a single brand, it is possible to find notebooks that use different voltages or plug sizes. For example, Dell has a standard plug size, but the Inspiron Minis are exceptions to this rule.
The stock power adapter that ships with your notebook supplies voltage at a fixed setting. This is not so for the external batteries. In order to deliver the multiple voltages required by different devices, they must also be capable of outputting different voltages.
There are a couple of ways to do this. The easiest way is to use a voltage converter controlled with a manual switch. Some companies choose to go a step further by using a sense resistor in the adapter tip. The sense resistor drops the voltage as current crosses its path. The small voltage drops are fed to a simple comparator circuit, which is then used to control the VDC output from the power supply.
If the resistor is in the tip, there is an additional layer of protection because you cannot force an incorrect voltage over a plug. Physical switches give you more control, but there is a chance that you'll choose an incorrect voltage and damage your notebook.
The way voltage gets to your notebook is important to understanding how an external battery can affect run time. Say your internal laptop battery yields two hours and your external battery offers an additional two hours. If your notebook is at 50% and your external battery is at 100%, this doesn't mean you get three hours total. There is an efficiency loss involved whenever you make an energy transfer, and you see this happen whenever the external battery charges the internal battery. This ineffiiency is less than what you see with an AC to DC conversion if you were to use a UPS, but it is there all the same. Remember that this only applies during a transfer of energy from battery to battery. If your notebook was at 100% and external battery was at 50%, you would see three hours total.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: External Batteries: How Do They Work?
Prev Page Background: The Technical Stuff Next Page Amstron MedXP 140 And 300-
lashabane Excellent article. I had an idea that this stuff was out there but never really bothered to look. If the 4-5 hours I get from my Asus 1215t begins to not cut it, I now know where to look. Thanks!Reply -
zodiacfml I did not understood any of the technical reading especially the part about the desktop PSU.Reply
At one point, it is stated that AC adapters have higher voltage than the battery on a notebook so that it can be charged. Then, how can a external battery damage a notebook's electronics with a higher voltage (only if it's too high)?
It is not stated how to set the external battery voltage correctly. What then is the correct voltage? Correct me but I believe the voltage has to be equal that of notebook battery.
-
burnley14 It's pretty remarkable that after page 2 I could guess who the author of this article was (without looking of course) due to the thoroughness and good grammar/lack of typos. Hats off to you yet again, Mr. Ku. Job well done as always.Reply -
nukemaster zodiacfmlI did not understood any of the technical reading especially the part about the desktop PSU.At one point, it is stated that AC adapters have higher voltage than the battery on a notebook so that it can be charged. Then, how can a external battery damage a notebook's electronics with a higher voltage (only if it's too high)? It is not stated how to set the external battery voltage correctly. What then is the correct voltage? Correct me but I believe the voltage has to be equal that of notebook battery.Your guess is actually right. The battery with its voltage set too high can damage the notebook.Reply
If you need to know the voltage required, you just check on your laptop AC adapter or power brick. It is not always the same as the battery.
For instance, a Compaq R3000 has an 18.5 volt AC->DC(120w) power supply and its battery is only 14.5 volts. The voltage regulators in the laptop(in the charging system) it self cut it down to the needed 14.5-15volts to charge the battery.
Also note that the AC adapter does NOT spit out AC it in fact spits out DC(it has a rectifier to convert AC to DC).
As you can see by this picture(you have to click the link), The adapter takes in AC 120V and spits out DC 18.5V. AC is shown with a ~ and DC with a --_---_-- cant make it on here, but you get the point.
http://img269.imageshack.us/img269/1950/powerw.jpg -
Luscious Quite a different experience on my end testing the Energizer XP8000 and XP18000.Reply
For my smartphone and MiFi, the XP8000 just can't be beat. 5x runtime guarantees me 20+ hours of 3G broadband and week-long phone use. Being barely bigger than a Blackberry, I can effortlessly stash the XP8000 on my belt, and charge my smartphone while I walk.
The XP18000, on the other hand, was a huge disappointment. Using a Toshiba NB305 netbook, it was incapable of recharging the factory 6-cell battery while powered on, and could not provide 2 full charges while powered off. For my usage scenario, that's a failure, as I plug in the external battery when my netbook hits 3% critical, right before Windows does a force shutdown, allowing me to continue working.
Using this deplete-charge-deplete approach SHOULD allow me 14+ hours of continuous power-on time, except that even the beefy XP18000 couldn't get through 1 netbook charge. Had it been capable of providing one full charge powered on, or two full charges powered off, I would have recommended the XP18000 as well.
http://lgponthemove.blogspot.com/2010/07/accessory-corner-3-energizer-xp18000.html -
a_fortiori Nice article. I wonder if these units can be used as a mini-ups for equipment like a NAS, routers and modems. It would be great if you could wire these with the NAS, and be sure that a power outage wouldn't damage the NAS. Considering that the NAS units typically consume much less power than a notebook, these should be able to cover 4-5 hrs of power outage (?) Any thoughts?Reply -
junixophobia shineon2010Very good info , alot of products that im having second thoughts about.Reply
Just buy an automatic inverter that works for hours with a car battery