CORE Or Boost? AMD's And Intel's Turbo Features Dissected
Intel arms its Core i5 and Core i7 CPUs with Turbo Boost. AMD's hexa-core Phenom II X6 chips sport Turbo CORE. Both technologies dynamically increase performance based on perceived workloads and available thermal headroom. Which one does the better job?
Benchmark Results: Efficiency
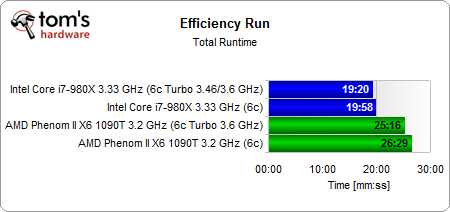
The runtime for our full efficiency suite decreases a bit more on the AMD platform, as there are more applications taking advantage of the company's Turbo CORE implementation than Intel's more meager Turbo Boost acceleration.
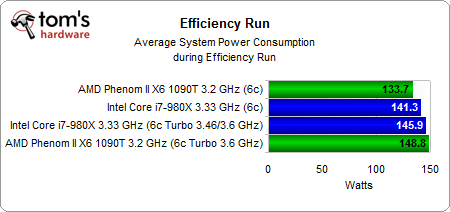
Average power consumption is much higher on the AMD system with Turbo CORE enabled, though.
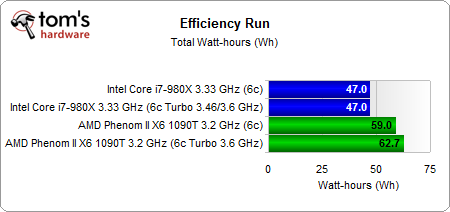
The total power used is exactly the same on the Intel system. This is interesting because the Core i7-980X with Turbo Boost is still faster. AMD’s Turbo CORE-enabled Phenom II X6 delivers more performance, but it requires more power to deliver it.
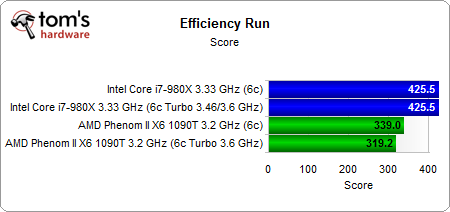
In the end, the Intel chip's efficiency stays constant. The total power used is exactly the same, but the average power is higher during the workload. As a result, the efficiency is identical. This is like reaching your destination faster in a car without changing your mileage per gallon. AMD’s Turbo implementation sacrifices power efficiency. Runtime decreases, but average power and total power used increase at a higher proportion.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Benchmark Results: Efficiency
Prev Page Benchmark Results: Power Consumption Next Page Conclusion