Last Passing Maneuver: Tualatin 1266 With 512 kB Versus Athlon And P4
10 New Pins
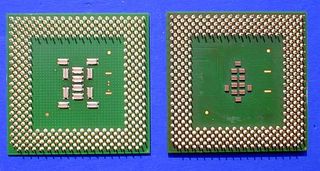
On the left, the PIII Coppermine, on the right the PIII Tualatin: the 370 pins are a constant. Only the SMD components are smaller than the predecessor's.
Intel already did it once when moving from the Celeron/Mendocino 533 (black PPGA case) to the Celeron/Coppermine 533A (green FCPGA case): new pins required modifications on motherboards. The Tualatin has pins that have been altered too. The pin count of the 370 has not been tinkered with, because that would have meant a new socket.
The chart below shows the pin IDs that were replaced by Intel. Unlike Coppermine, all others retain the same significance. The AF36 is one of the important pins. Its voltage functions to allow the chipset to recognize the processor type. If the AF36 has Vss voltage, then it is a PIII Coppermine; otherwise, it is a Tualatin that occupies socket 370. Depending on the condition, the FSB buffer mode on the i815 chipset and the appropriate Vtt voltage (1.5 or 1.25V) are set.
| Pin | PIII Coppermine | PIII Tualatin | Descripton for Tualatin |
|---|---|---|---|
| AF36 | Vss | NC | for CPU type detection |
| AB36 | VccCMOS | Vtt | pull to Vtt |
| AG1 | Vss | Vtt | switch between Vtt and Vss, depending on AF36 |
| AK4 | Vss | VTTPWGRD | pull to VTTPWRGD with 1 kOhm resistor |
| AK22 | GTL_REF | VCMOS_REF | GTL_REF=VCMOS_REF=1.0V; divert 1.0V on VCMOS (1.5V) |
| AK36 | Vss | VID[25mV] | pull to VID[25mV] |
| AN3 | Vss | DYN_OE | pull to Vtt with 1 kOhm resistor |
| AM2 | RESET# | NC | Not connected |
| X4 | NC | Vss | pull to RESET# with 1 kOhm resistor |
| AJ3 | Vss | RESET# | Not connected |
Stay on the Cutting Edge
Join the experts who read Tom's Hardware for the inside track on enthusiast PC tech news — and have for over 25 years. We'll send breaking news and in-depth reviews of CPUs, GPUs, AI, maker hardware and more straight to your inbox.
Current page: 10 New Pins
Prev Page Tualatin - Shadow Boxer Next Page B-Stepping With The I815/SolanoMost Popular



