AMD Ryzen 7 1700X Review
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Power Consumption And Temperatures
Direct Comparisons of Power Consumption
Similar to our performance numbers, we re-ran the 1800X review's power data to reflect the continual improvements being made to motherboard firmware.
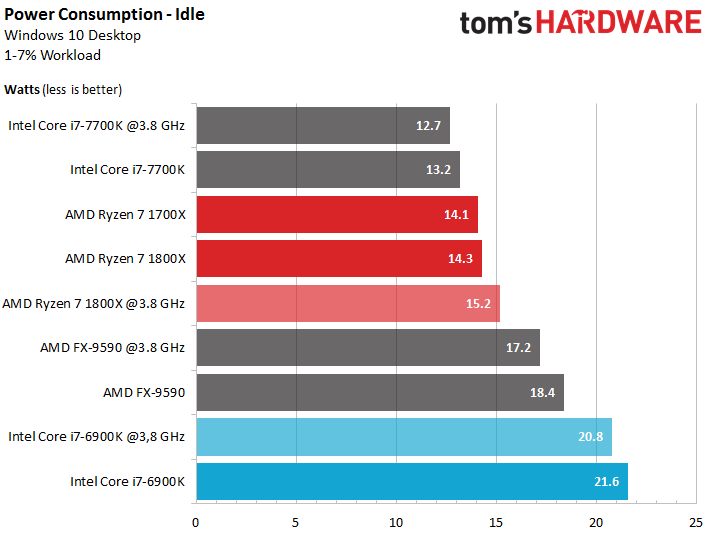
Let's start by looking at idle power consumption. Intel's overclocked Core i7-6900K turns in a better result than the stock configuration because we also reduced the one-core Turbo Boost frequency.
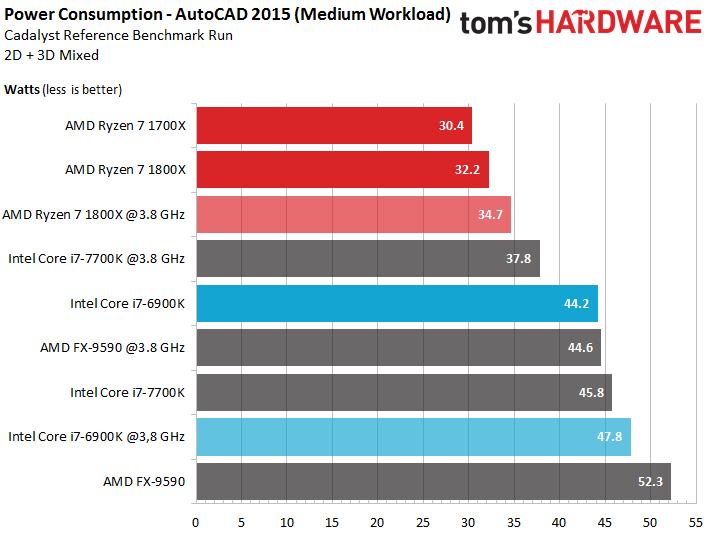
The 95W AMD CPUs clearly use less power in our combined CAD benchmark. When we weigh average performance against power consumption, however, the eight-core CPUs from AMD and Intel are fairly similar.
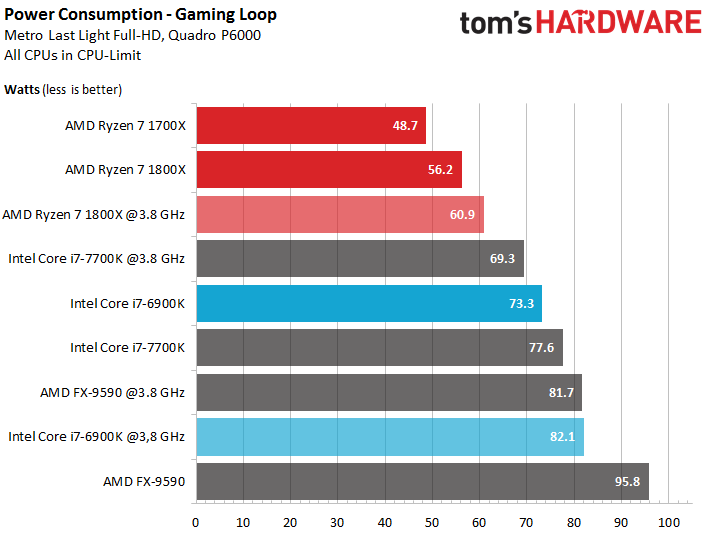
The same story applies to our measurements in games, where Ryzen 7 blows away the Core i7s. It's been a long time since AMD was at least equal in terms of efficiency.
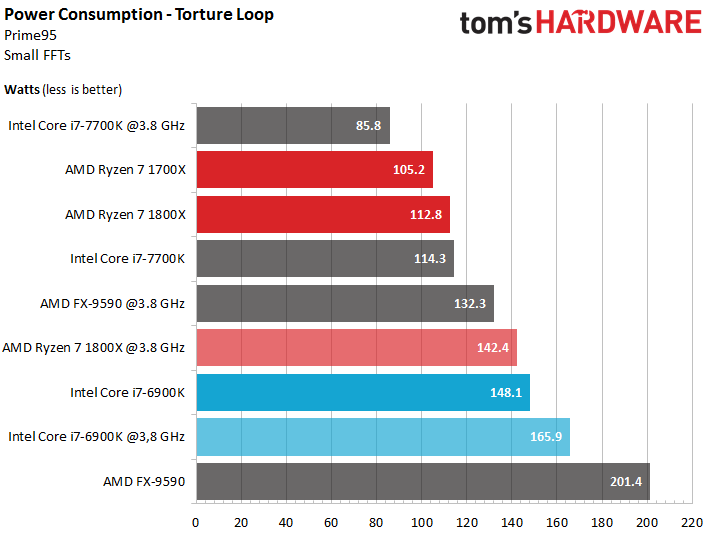
The 3.8 GHz Ryzen 7 sucks down more than 140W , but the Core i7-6900K is even worse at 166W. The Core i7-7700K down-clocked to the same frequency uses a conservative 86W or so.
Based on AMD's technology briefings, we know it has more granular control over clock rate. And it's notable that the 95W Ryzen 7 1700X we're reviewing today uses less power under our stress test than Intel's 91W Core i7-7700K. It takes a significant underclock to put the Kaby Lake flagship in first place.
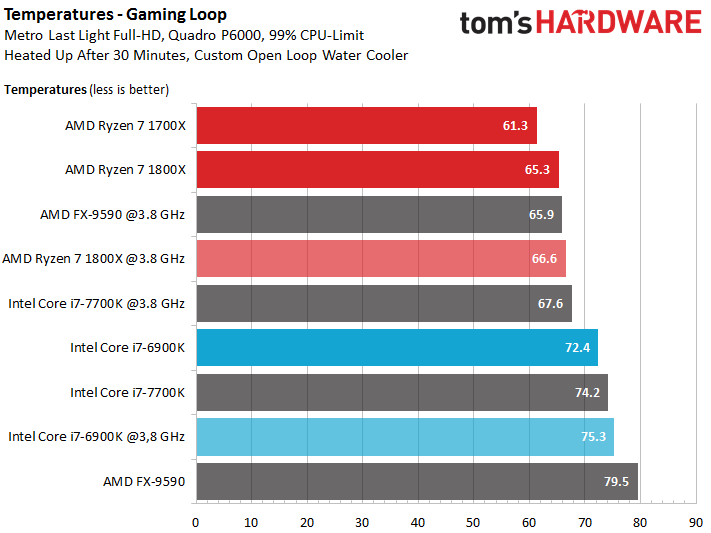
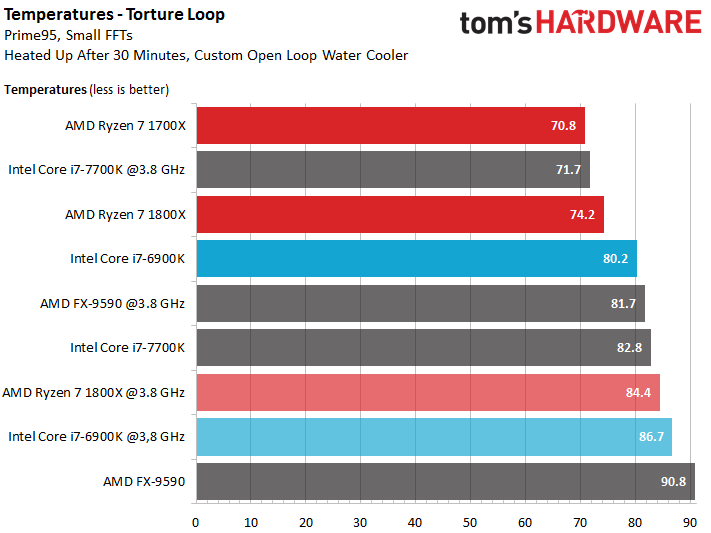
Temperatures
We optimized our CPU cooler for Socket AM4 by using two nuts between the spring and bracket to increase force on the package to 0.4Nm. That is why these results differ from those in our launch article, where we only used washers.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
The temperatures we recorded for the FX-9590 are a bit uncertain, since AMD’s older Bulldozer CPUs don't measure with 100% confidence. Moreover, the Ryzen 7 and Core i7 CPU readings aren't exactly comparable; both companies employ different sensor approaches.
Intel's Core i7-7700K is the only processor in our test field handicapped by cheap thermal paste between its die and heat spreader. Thankfully, AMD solders Ryzen's heat spreader, which results in good thermal transfer. This naturally shows up in the relationship between power converted to heat.
Enthusiasts should be happy with Ryzen's power consumption and its resulting waste heat.
Current page: Power Consumption And Temperatures
Prev Page Workstation And HPC Benchmarks Next Page Conclusion
Paul Alcorn is the Editor-in-Chief for Tom's Hardware US. He also writes news and reviews on CPUs, storage, and enterprise hardware.
-
Ergosum Whoever runs PR at AMD needs to reevaluate their methods. The 1800's and 1700's are very solid products, but for some reason were shadow marketed--letting rumor define the target application sets.Reply
AMD should have had a strong positive campaign on where these chips do well. Specific. Timely. They would have gathered some gamers who wanted to brag about handbrake performance or some-such. Instead they let the market build fairy castles in the sky about gaming-specific performance, and so (again) lost a great deal of goodwill and trust. -
hannibal The problem is that the market made those cloud castless, not the AMD... it is hard to AMD to say users not to speculate. Every information that AMD did give out was confirming that Ryzen was going to be really good multicore performer, and we all know that very few game use more that teo or three threats, so the extra 4-6 cores that Ryzen has normally Are useless I. The games, so any Intel 2-4 core prosessor wa going to better in the games if They would run in higher freguences that Ryzen and AMD very clearly tell us that 3.8 was the very near the top of the prosessor speed.Reply
If and when games start supporting 8 cores the 1700 is super good perfomer in the games too, but if and most propably because the situation stays the same. 2-4 more powerfull cores is always better in games that having more of them.
It seems that people now know games really poorly if They expected the Ryzen has any chance in those.
Ryzen 1500 (four cores) is as fast in the games than 1800X is and 1500 is much cheaper.
http://www.techspot.com/review/1360-amd-ryzen-5-1600x-1500x-gaming/ -
TechyInAZ Good review. Can't wait until software devs and motherboard manufactuer's get better optimized softwares and BIOS's so Ryzen isn't constantly dealing with this problem anymore.Reply -
dstarr3 Reply19481950 said:Conclusion: Ryzen still sucks.
It's not that Ryzen sucks, it's that Ryzen was meant to compete with Xeon CPUs, which it does very well. Gamers should look elsewhere, but for some reason, gamers are the ones that got most excited about these CPUs. -
elbert I wouldn't suggest either a 1070 nor the 1080 on 1080p. Probably should have tested with a more normal 1060 6GB at that resolution. Those willing to pay high prices for both the CPU and GPU should be running at 1440p. The game benchmarks are unnaturally skewed.Reply
The biggest thing to look at in the game benchmarks is how unutilized the Ryzen CPU's are. We will probably see the Ryzen R5 quads running the same FPS for a few hundered less then all but the old 8350 on April the 11th.
Also it looks like AMD is gearing up a new socket with 8, 12, and 16 cores on an X390 motherboard. At the current pricing the 16 core could be lower priced than Intel's over priced 6900 8 core. -
Achaios ?ll this talk about games supporting more than 4 cores is really a COMPLETE WASTE OF TIME.Reply
46.19% of Steam Gamers own 2-Core CPU's and 47.74% of Steam Gamers own 4 Core CPUs. No Game Studio is going to waste resources and money on optimizing games for more than 4 cores in the foreseeable future, if ever.
According to the same survey, only 0.24% of gamers own octacore CPU's. A little less than this is the presence of AMD Ryzen CPU's in the gaming market. Almost nonexistent.
I wish I was trolling. -
Oranthal Why did you only test 1080p performance? Most people who would consider these CPUs run an RX-480 or greater GPU if they are gaming ($300+ is still the premium market). Other reviews show the gaps shrinking or disappearing with greater resolutions as the bottlenecks are at the GPU where most die-hard review reading gamers will actually be limited.Reply -
Oranthal Reply19482020 said:I wouldn't suggest either a 1070 nor the 1080 on 1080p. Probably should have tested with a more normal 1060 6GB at that resolution. Those willing to pay high prices for both the CPU and GPU should be running at 1440p. The game benchmarks are unnaturally skewed.
The biggest thing to look at in the game benchmarks is how unutilized the Ryzen CPU's are. We will probably see the Ryzen R5 quads running the same FPS for a few hundered less then all but the old 8350 on April the 11th.
Also it looks like AMD is gearing up a new socket with 8, 12, and 16 cores on an X390 motherboard. At the current pricing the 16 core could be lower priced than Intel's over priced 6900 8 core.
100% spot on. I would of skipped my comment had I seen this when I started writing it.