Asus MG278Q 27-inch QHD FreeSync Gaming Monitor Review
Recently we checked out Asus' MG279Q, a stunning-looking 27-inch IPS gaming monitor with FreeSync, 144Hz and a premium price. Today we're reviewing a cheaper alternative -- the TN-based MG278Q.
Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
Color Gamut And Performance
For details on our color gamut testing and volume calculations, please click here.
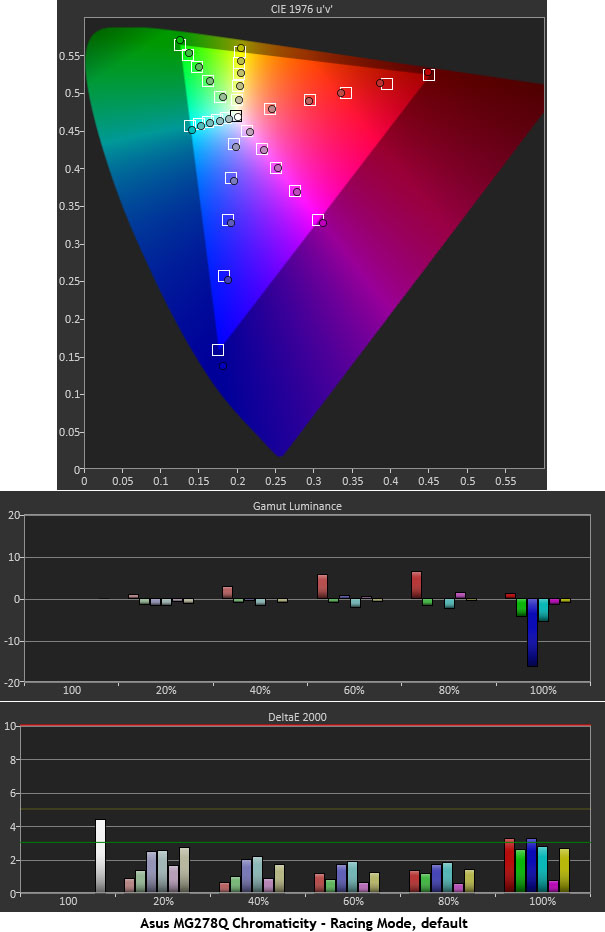
By altering the gamma tracking, different color saturation profiles can be achieved. Each picture mode on the MG278Q does this to varying degrees. Racing comes close to the desired gamut in its unadjusted state. As we concluded in the grayscale test, calibration is beneficial but not absolutely necessary. Luminance levels are all where they should be. Reds slight under-saturation and blue's slight over-saturation are both compensated for properly. None of the errors here are visible.
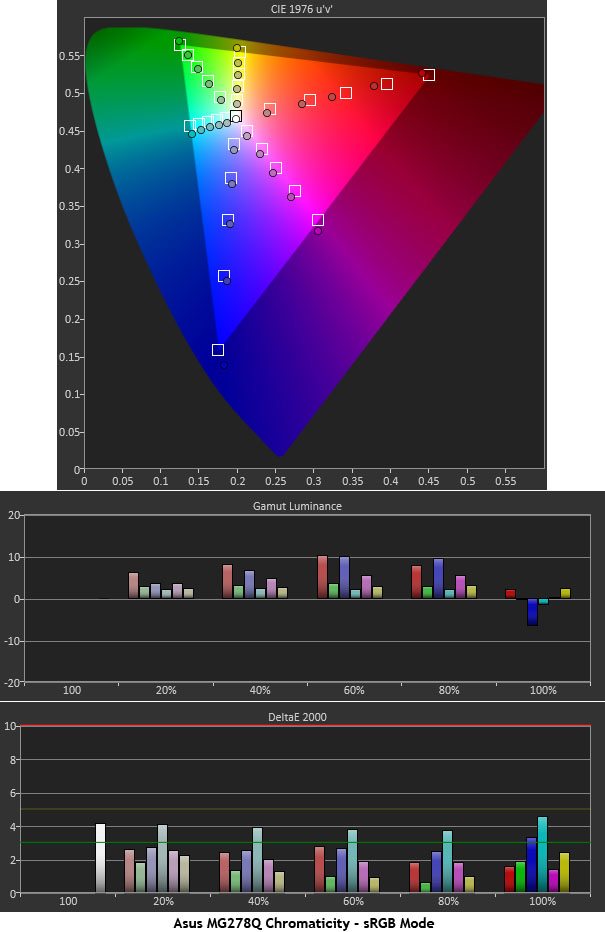
sRGB deviates a little thanks to a cooler white point and altered gamma curve. It's still a perfectly usable mode however. Our only real complaint is its lack of a brightness adjustment. Otherwise color accuracy is in the acceptable if not ideal range.
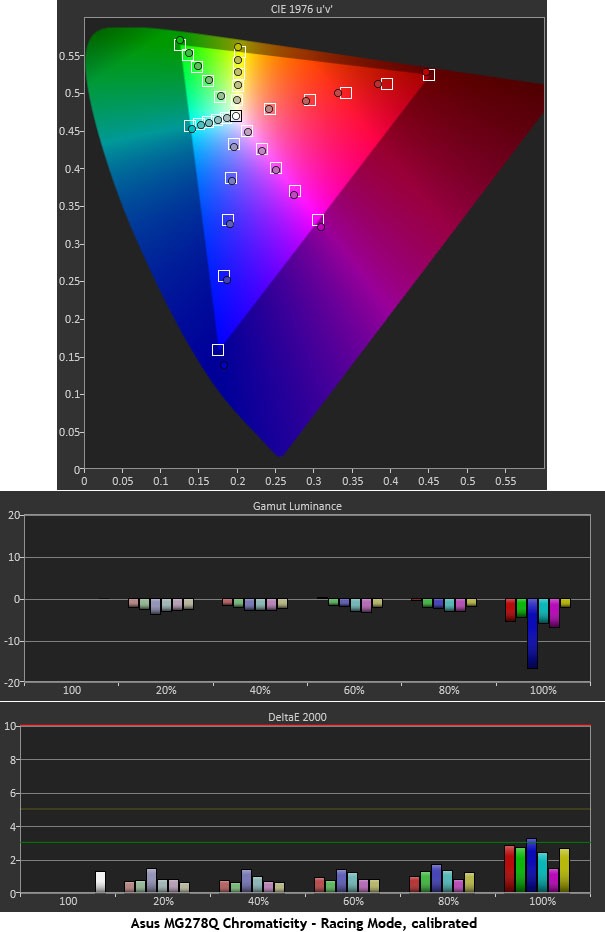
Calibration improves color accuracy enough that we think it's worth the effort. Racing mode grays out the saturation and flesh tone sliders but they can only adjust specific parameters that don't help the overall picture quality as much. Remember to try our suggested settings on page three if you don't have the proper instruments.
Now we return to the comparison group.
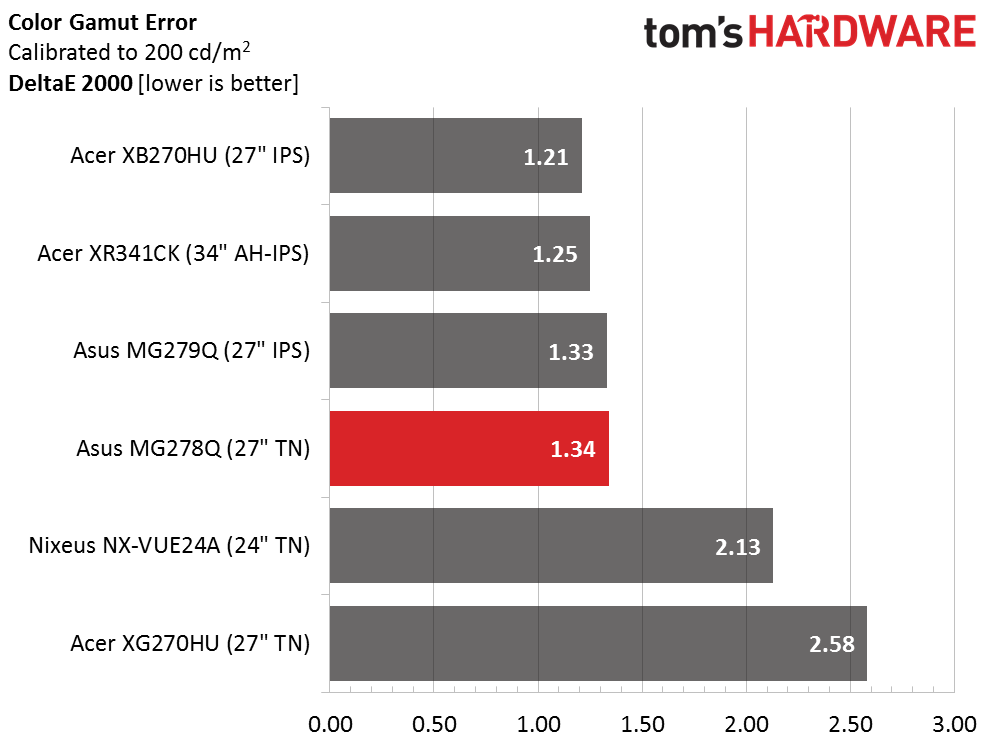
The MG278Q is in the top-tier of screens here today. It also compares well to gaming and business-class monitors as a whole. While some users complain about TN's color quality, we're not seeing any issues here today.
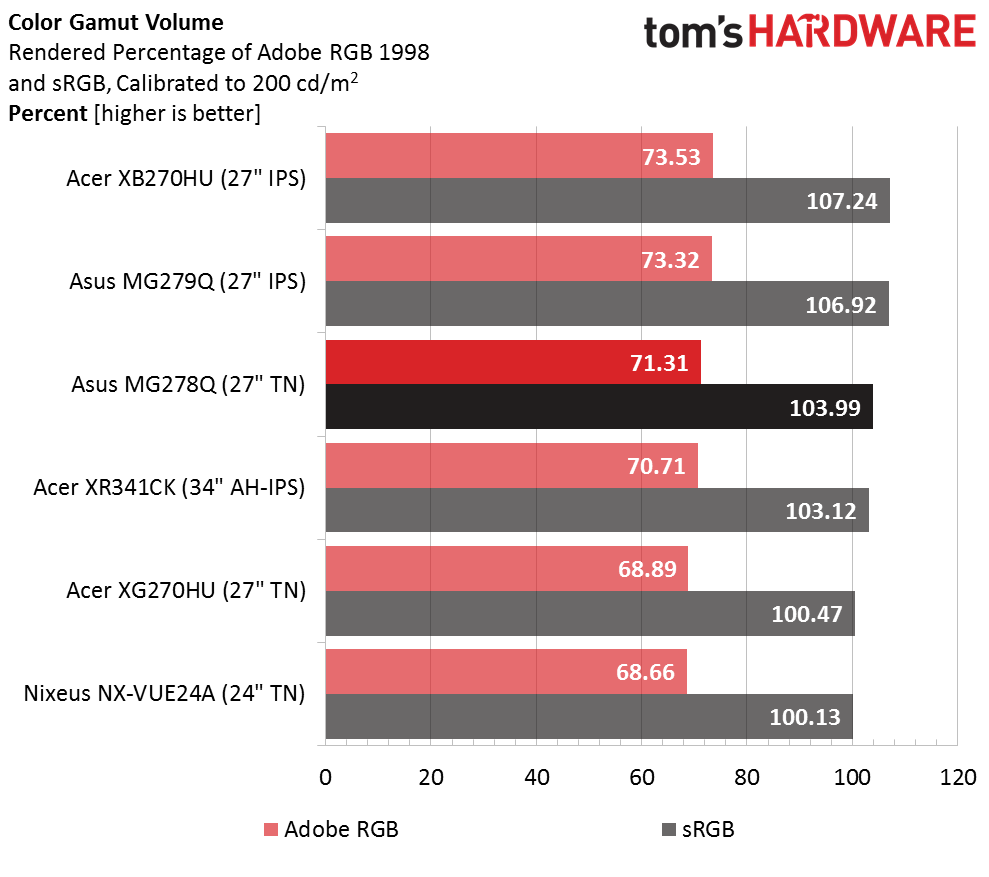
Gamut Volume: Adobe RGB 1998 And sRGB
Thanks to some bonus blue, the MG278Q exceeds 100 percent of the sRGB gamut volume. This doesn't affect gaming or general performance but if you plan to add this display to a color-critical workstation, you'll need to adjust your printer and camera profiles accordingly.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: Color Gamut And Performance
Prev Page Grayscale Tracking And Gamma Response Next Page Viewing Angles, Uniformity, Response, Lag, And FreeSync
Christian Eberle is a Contributing Editor for Tom's Hardware US. He's a veteran reviewer of A/V equipment, specializing in monitors. Christian began his obsession with tech when he built his first PC in 1991, a 286 running DOS 3.0 at a blazing 12MHz. In 2006, he undertook training from the Imaging Science Foundation in video calibration and testing and thus started a passion for precise imaging that persists to this day. He is also a professional musician with a degree from the New England Conservatory as a classical bassoonist which he used to good effect as a performer with the West Point Army Band from 1987 to 2013. He enjoys watching movies and listening to high-end audio in his custom-built home theater and can be seen riding trails near his home on a race-ready ICE VTX recumbent trike. Christian enjoys the endless summer in Florida where he lives with his wife and Chihuahua and plays with orchestras around the state.
-
Rishi100 I am flummoxed why even at this stage, the displays are being churned out with HDMI 1.4 and Displayport 1.2 standards. They should have been HDMI 2 with HDCP 2.2 and DP1.3.Reply -
TeamColeINC From what I've seen in reviews so far, then TN model is better anyway. But I would think ASUS fixed all the issues that people were reporting with the IPS model...Reply -
10tacle The last time I tried an ASUS 1440p panel was with their PB278Q (60Hz IPS). The first one I got had terrible back light bleed on the left side and two dead pixels right in the middle. Couldn't live with that. So I returned it and got another. The second one was sealed up on backlight bleed (good enough for the typical PLS/IPS anyway) but had four dead pixels, two which were close together on the center right side and the other two in different spots but in the general viewing area. Again, couldn't live with it and returned for my money back.Reply
I hope their quality control has improved, because for a $500+ monitor, any dead pixels and manufacturing tolerance defects are unacceptable. I paid a little more for a Dell U2713HM and have been happy ever since. I'll be in the market for a 1440p G-sync next year as an SLI 970 owner and would not rule out ASUS if they have improved their quality control. One thing I am not clear on is if you can select custom Free-Sync or G-Sync frequencies to better match your GPU power beyond factory monitor Hz settings (90Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz). -
alextheblue ReplyAt speeds below 40fps, you'll need to turn on V-Sync to prevent tearing, though by that point stutter is the bigger problem. It's better to either reduce resolution or turn down the detail level to keep frame rates above 40.
Uh, what about turning on LFC? LFC will work on monitors with a good variable refresh range such as this Asus unit. I'd like to see that tested for those cases where you dip in frames occasionally.
One thing I am not clear on is if you can select custom Free-Sync or G-Sync frequencies to better match your GPU power beyond factory monitor Hz settings (90Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz).
Wait, what? As long as you're within the variable refresh rate range, you're good to go. If you want to save power and reduce the framerate on a low-demand (old) game something like FRTC should work if there's no in-game cap. -
10tacle Reply17162561 said:One thing I am not clear on is if you can select custom Free-Sync or G-Sync frequencies to better match your GPU power beyond factory monitor Hz settings (90Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz).
Wait, what? As long as you're within the variable refresh rate range, you're good to go. If you want to save power and reduce the framerate on a low-demand (old) game something like FRTC should work if there's no in-game cap.
No what I'm talking about are complaints about (and this was from G-sync users) that they couldn't set a custom refresh rate to something like 100Hz or 110Hz in the Nvidia control panel on a G-sync monitor to better match their GPU power FPS and cap it. Maybe something's changed or they didn't know what they were talking about (or doing).
I don't have one so I can't comment. I overclock my 1440p monitors to 75Hz (Dell) and 90Hz (Crossover) and cap frames accordingly, but just have never been clear on what that meant to a G-sync monitor that advertises 120Hz/144Hz capability.
-
M for Moartea Reply
No what I'm talking about are complaints about (and this was from G-sync users) that they couldn't set a custom refresh rate to something like 100Hz or 110Hz in the Nvidia control panel on a G-sync monitor to better match their GPU power FPS and cap it. Maybe something's changed or they didn't know what they were talking about (or doing).
I don't have one so I can't comment. I overclock my 1440p monitors to 75Hz (Dell) and 90Hz (Crossover) and cap frames accordingly, but just have never been clear on what that meant to a G-sync monitor that advertises 120Hz/144Hz capability.
I'm not sure I fully understand your concern but, if I may, I'll give it a try.
As a user of Asus PG278Q (with G-sync) for a year now, I can tell you this much:
G-sync, much like FreeSync, works within a frame rate range, depending on the monitor and not the adaptive sync technology behind it, in my case within 30-144Hz. Between that frame rate range, the refresh rate is variable and depends on how many FPS your GPU can push.
This is where the similarities between the two stop because outside of that range the two technologies behave differently. Below the minimum range, 30 FPS in my case, the G-sync module automatically displays the same frame twice, making the frame rate appear double than what it is and the gameplay feel smoother. At the other end, G-sync module automatically caps your frame rate to the maximum refresh rate of your monitor (144 in my case).
That being said, having nothing to do with these adaptive sync technologies, Radeons do have a frame rate target control feature in the Catalyst control center (or whatever it's called nowdays) for power savings reasons, feature that you don't have as a Nvidia user.
Now, regarding your concern, a custom refresh rate simply defeats the purpose of having an adaptive sync technology and, outside of power savings reasons, I fail to see how a custom refresh rate target would help since G-sync (and FreeSync for that matter) already cap the refresh rate of your monitor "to better match their GPU power FPS".
If you prefer a custom refresh rate, you can chose do simply disable G-sync and set your (G-sync enabled) monitor to a fixed refresh rate (in my case I have the following options: 24, 60, 85, 100, 120, 144 Hz).
I hope that was helpful. -
Verrin ReplyAt speeds below 40fps, you'll need to turn on V-Sync to prevent tearing, though by that point stutter is the bigger problem.
This technically isn't true any more, if you are using the Crimson driver and have a panel with a maximum refresh rate that is 2.5 times greater than the minimum (e.g. 144Hz panels).
AMD refers to this new tech as Low Frame Rate Compensation (LFC), and it effectively does the same as Nvidia's solution (although by different means) by duplicating frames to maintain the refresh rate above a minimum refresh value (such as 40Hz). I've been playing around with it on my 390X and my Acer XG270HU and it's been working great, no stutter or hitching, just the usual expected loss in fluidity from going that low in the first place. -
picture_perfect Tearing happens when fps are higher than hz (multiple frames per refresh appear as horizontal tears in time)Reply
Stutter/Judder happens when fps are lower than hz (multiple refreshes per frame appear as double vision judder)
To sync the two:
Freesync/G-sync adjusts a monitor's hz to match fps.
V-sync adjusts fps to match a monitor's hz. -
Andrew Pacely This is cool and all... but where's that new 34 incher they revealed last September?Reply -
jdwii Threw up a little when i heard TN, little to no excuse anymore not to own a IPS monitor since latency is as low as 4ms and i bet 99.9% of you guys can't tell the differenceReply