Here's What A Ryzen 7 7800X3D Looks Like With An Infrared Camera
AMD's 2nd Gen 3D-VCache smiles for the camera
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
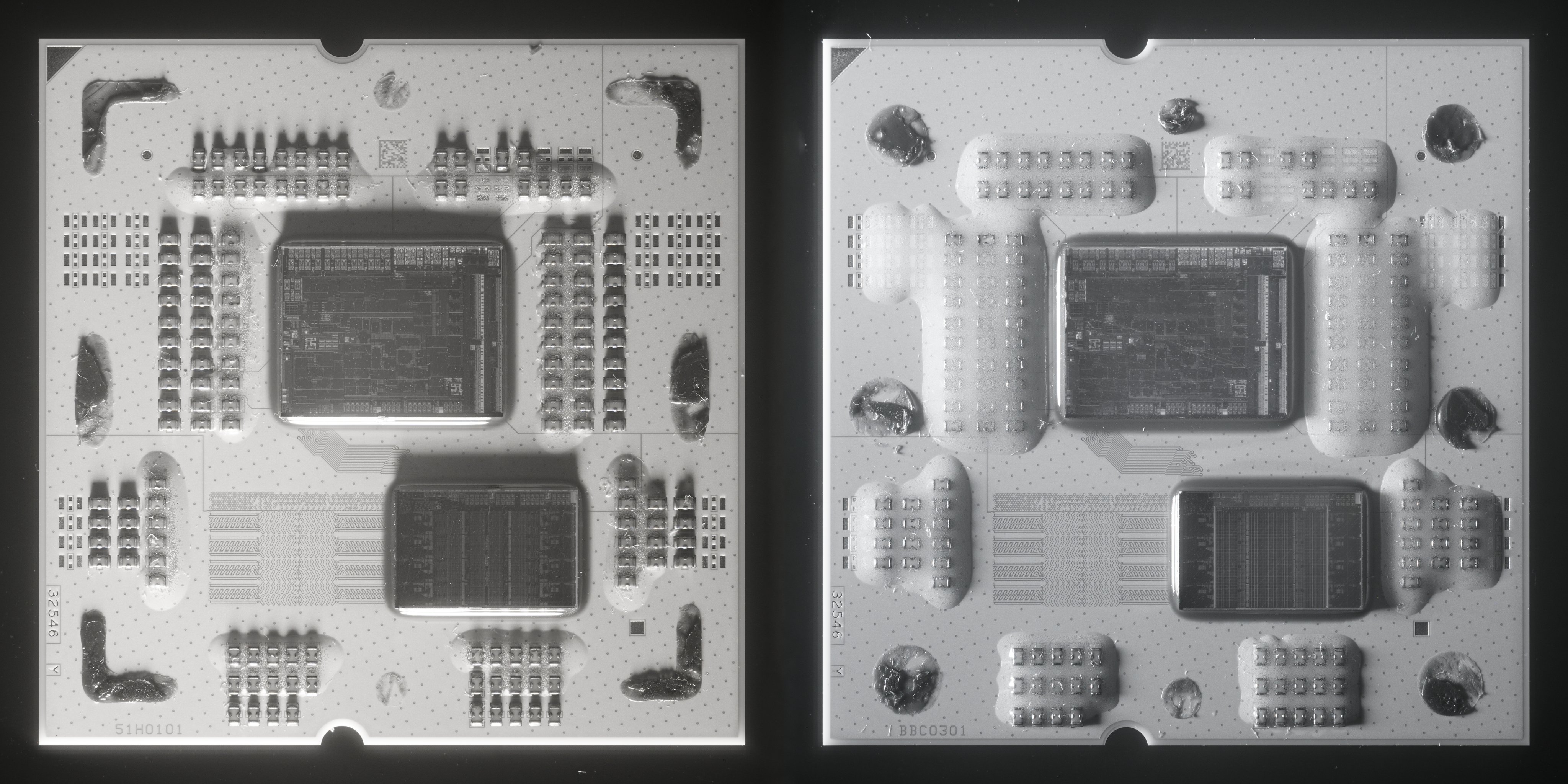
Chip detective @FritzchensFritz has posted an excellent image comparison between the Ryzen 5 7600 and a Ryzen 7 7800X3D featuring shots taken with an infrared camera. The infrared images show us the inner layers of AMD's Ryzen 7000 and 7000X3D processors, revealing the subtle architectural differences between the different chips.
The differences between both CPUs can be difficult to detect at first glance, but once you know what to look for, the differences are obvious. The left CPU in the image represents the Ryzen 5 7600 (and Ryzen 7 7700), while the right represents the Ryzen 7 7800X3D.
Looking closer at the Core Complex Die (CCD) of each CPU (the bottom right die), you can see how AMD lays out the core and cache layout in its Ryzen 7000 processors. The four "squares" located on the left and right edges of the CCD represent the eight physical Zen 4 cores located on the chip, while the middle section holds the CPU cache.
Even though the Ryzen 5 7600 is a six-core part, you can tell the chip physically has eight cores according to the infrared image. This is because AMD only uses eight-core clusters in its Ryzen chips (for now), and disables cores when needed to make additional SKUs.
The middle portion of the CCD represents the CPU cache area, where the L1, L2, and L3 caches are located. This is where obvious changes can be seen between the 7600 and 7800X3D. The 7600 features a normal L3 cache configuration consisting of two 16MB caches unified into one 32MB cluster, while the 7800X3D looks completely different due to the "giant" 64MB slab of cache stacked on top of the bottom 32MB cluster (making it impossible to see the bottom 32MB cluster). You can learn the deep-dive details of this setup in our AMD Shares New Second-Gen 3D V-Cache Chiplet Details, up to 2.5 TB/s article.
You can also tell from the infrared image that the stacked 64MB cache partially covers the Zen 4 cores as well, due to the lithography differences between the 7nm SRAM 3D-VCache and the 5nm Zen 4 CPU cores. This is different from AMD's first-generation 3D-VCache CPU, the Ryzen 7 5800X3D, which had an even layer of stacked cache that only covered the bottom 32MB L3 cache cluster, and did not cover the cores, because both the stacked cache and Zen 3 cores featured the same 7nm lithography.
The Ryzen 7 7800X3D's uneven 3D-VCache does not affect performance as far as we know, but it did introduce additional engineering challenges for AMD, since it had to move the TSV connectors (powering the 3D cache), from the L3 cache die area on older Zen 3 designs to the L2 cache area on its Zen 4 chips. Ironically the 7800X3D's 3D-VCache chip is actually smaller and denser than the 5800X3D's, however, the 7800X3D's CCD is still too small for its newer 3D-VCache chip to fit within the die constraints afforded to the L3 cache only.
With and without AMDs 3D V-Cache pic.twitter.com/COyooAnDDyMay 19, 2023
For a refresher on AMD's latest 3D-VCache technology, be sure to check out our previous coverage here. But essentially, the Ryzen 7 7800X3D, Ryzen 9 7900X3D, and 7950X3D feature AMD's 2nd generation 3D-VCache technology, offering significantly faster and denser vertically stacked cache compared to its predecessor.
AMD's 3D cache design helps improve gaming performance and other cache-sensitive workloads by tripling the amount of cache the CPU has access to. This reduces the amount of time the CPU needs to access slower system RAM and keeps more data confined to the faster L3 cache, which improves performance and reduces latency.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Aaron Klotz is a contributing writer for Tom’s Hardware, covering news related to computer hardware such as CPUs, and graphics cards.
-
A Stoner If the 3d cache is 100% between the cores, it seems to me that the solution for the cooling requirements would be to step the heat spreader so that it is closer to the cores and thinner over the cache area. Less of the low performance TIM and more of the higher performance metal over the cores, and the cache is closer to the cooling all around.Reply