Under The Hood: 140 Chipsets Compared
The Basics: The Structure Of A Chipset
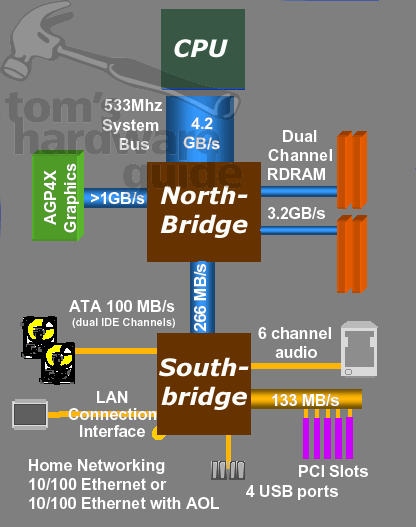
Essentially, each chipset consists of a Northbridge and a Southbridge. Some of the chipsets from SiS are exceptions, for example, the 735 and 645, both of which are based on a single-chip technology. The above scheme lets you clearly recognize how a traditional chipset works. The following components are connected to the Northbridge in a star-like constellation: the processor, the graphics interface, the RAM and the Southbridge. The largest amount of data is transferred between the CPU and the Northbridge - in our example, the maximum volume is 4.2 GB per second. The RAM is second in generating large amounts of traffic (here, we use a dual-channel Rambus interface as an example), with 3.2 GB per second. Less optimized in terms of bandwidth is the data transfer to the graphics interface, which, according to the AGP 2.0 standard, is above 1 GB per second.
The second chip of the chipset is the Southbridge, which is responsible for communicating with the peripheral devices. This includes PCI interfaces, IDE controllers for hard drives and DVD/CD ROMs, and USB controllers, as well as sound and LAN interfaces. The Northbridge and the Southbridge are connected to one another through a data channel. Here are a few examples: the VIA KT133A chipset accesses a PCI 33 transfer mode that achieves 33 MB/s. Starting with the VIA KT266 chipset, the V-Link with 266 MB/s is used, which is likewise accessed by ATIs IGP 320 chipset. At the moment, the highest theoretical data transfer rate is offered by the nForce chipset with Hypertransport and 800 MB/s. Intel's chipsets (845 and 850) with Hub Link V1.0 provide 266 MB/s. Bringing up the rear is the Taiwanese manufacturer ALi; this company still works with the outmoded PCI 33 protocol today, something which its competitors have long since filed away.
Here, we'd like to address a question asked by readers who use a RAID controller (Promise or HighPoint) in a setup consisting of an outmoded chipset that has much too low a transfer rate between the Northbridge and Southbridge. In this case, the internal data transfer of the chipset is at its limit, so there's no noticeable performance increase when you create a RAID configuration. In addition, the other components such as USB and sound reduce the bandwidth, as well.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Current page: The Basics: The Structure Of A Chipset
Prev Page Socket 423/478: Chipsets From VIA Next Page Curiosities: Onboard Memory, Dual CPUs, Graphics Memory