Why you can trust Tom's Hardware
To learn more about our PSU tests and methodology, please check out How We Test Power Supply Units.
Primary Rails And 5VSB Load Regulation
The following charts show the main rails' voltage values recorded between a range of 40 watts up to the PSU's maximum specified load, along with the deviation (in percent). Tight regulation is an important consideration every time we review a power supply because it facilitates constant voltage levels despite varying loads. Tight load regulation also, among other factors, improves the system’s stability, especially under overclocked conditions and, at the same time, it applies less stress to the DC-DC converters that many system components utilize.
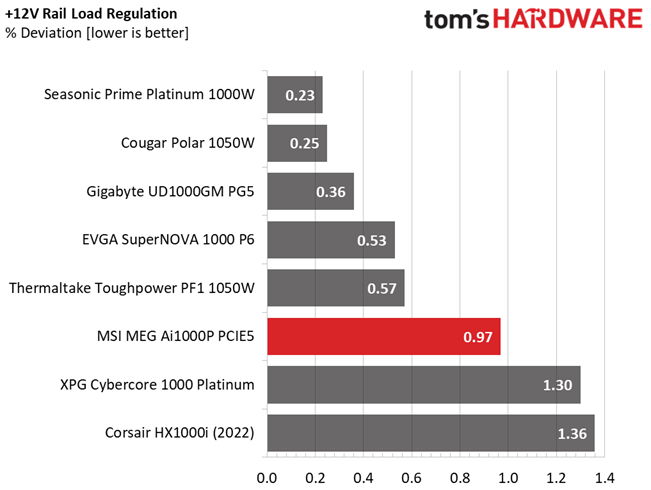
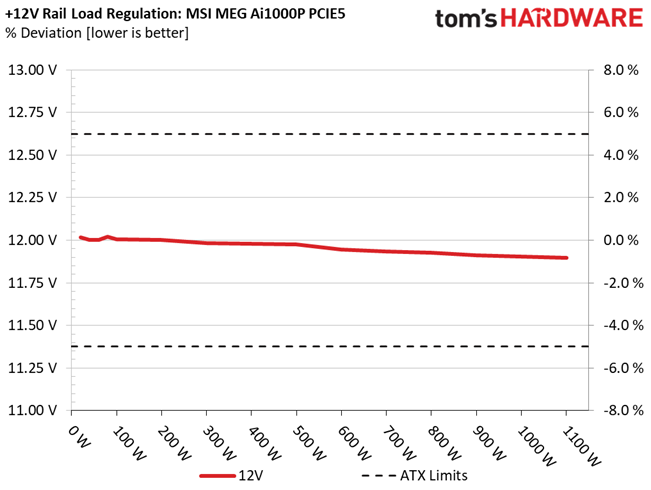
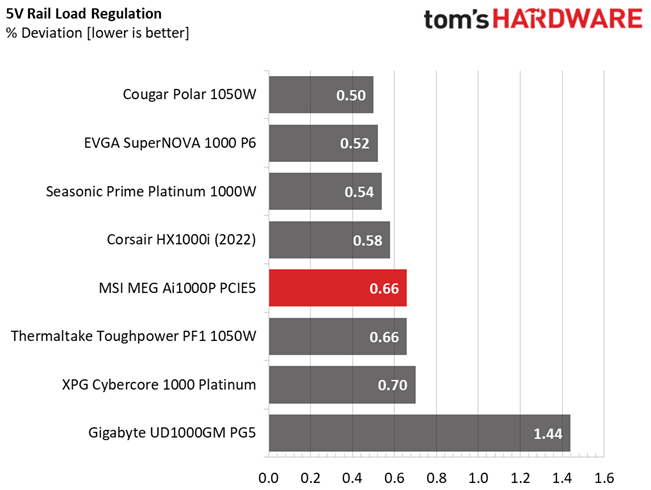
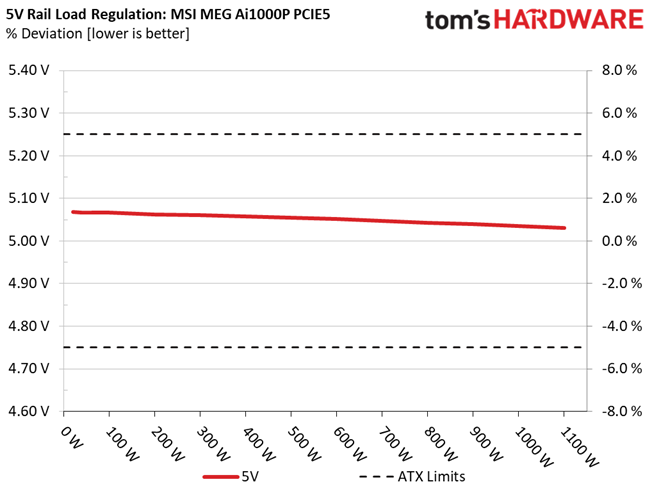
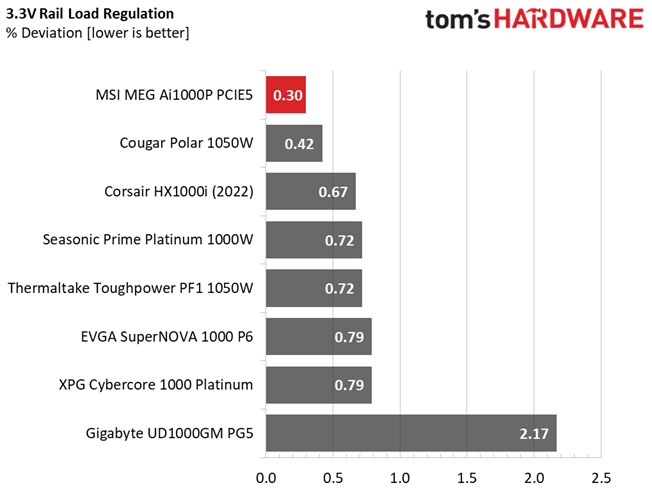
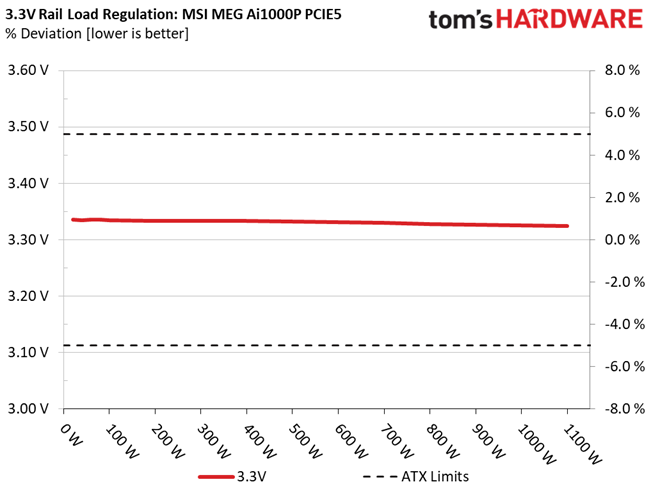
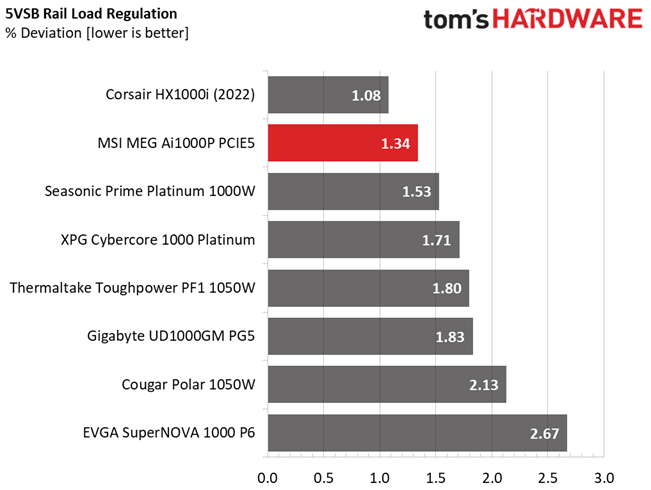
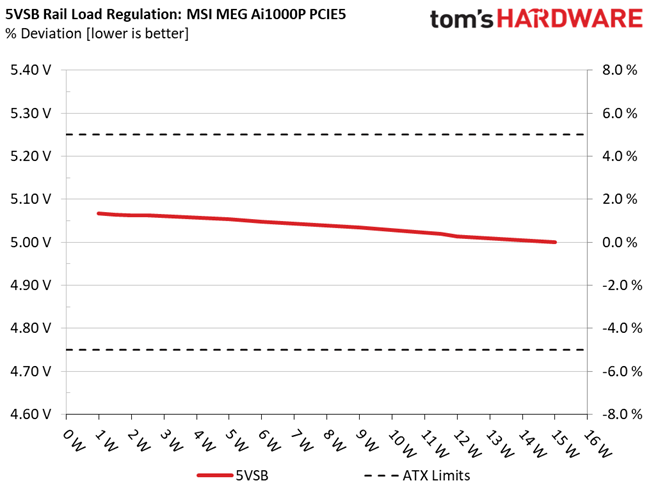
Load regulation is within 1% on all major rails, so it is pretty tight. It could be tighter at 12V, though.
Hold-Up Time
Put simply; hold-up time is the amount of time that the system can continue to run without shutting down or rebooting during a power interruption.
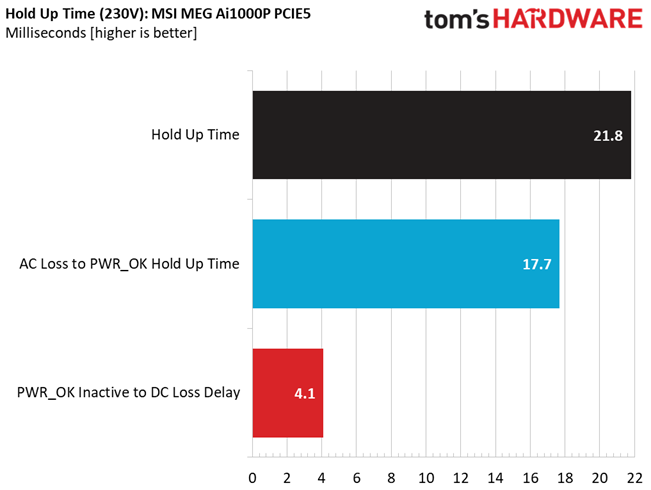
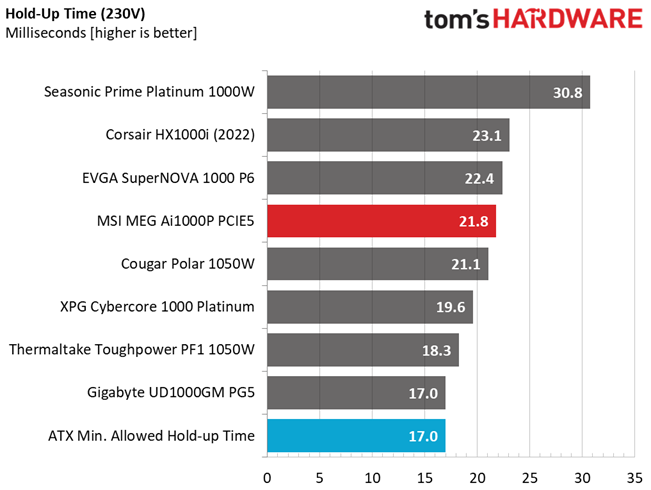
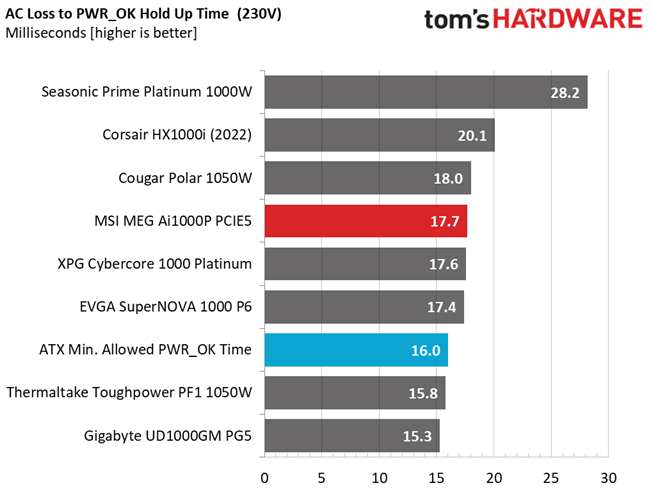
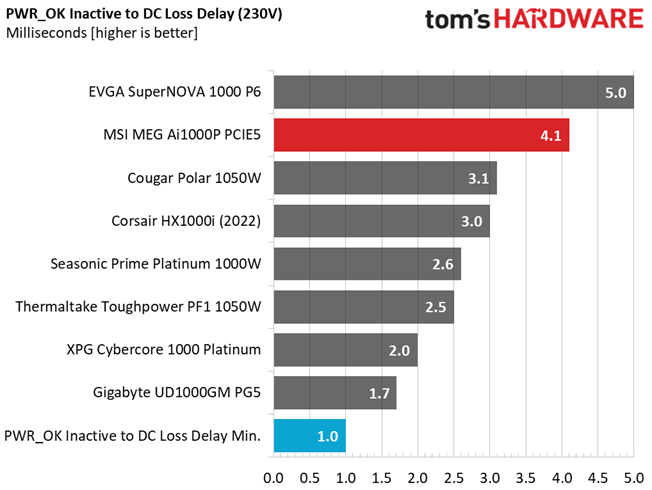
The hold-up time is long and the power ok signal is accurate and longer than 16 ms.
Inrush Current
Inrush current, or switch-on surge, refers to the maximum, instantaneous input current drawn by an electrical device when it is first turned on. A large enough inrush current can cause circuit breakers and fuses to trip. It can also damage switches, relays, and bridge rectifiers. As a result, the lower the inrush current of a PSU right as it is turned on, the better.
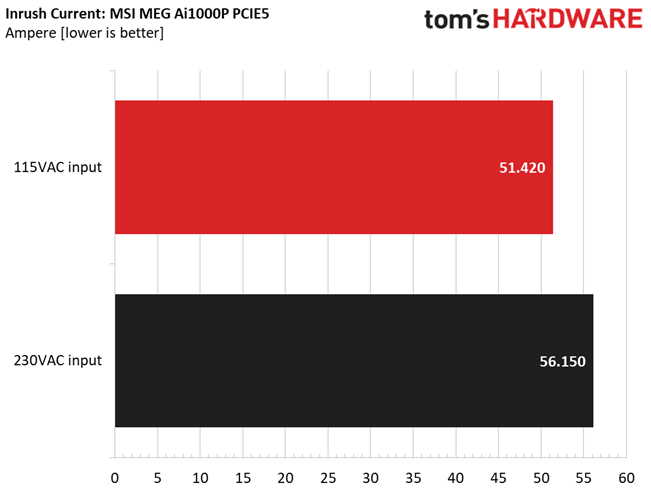
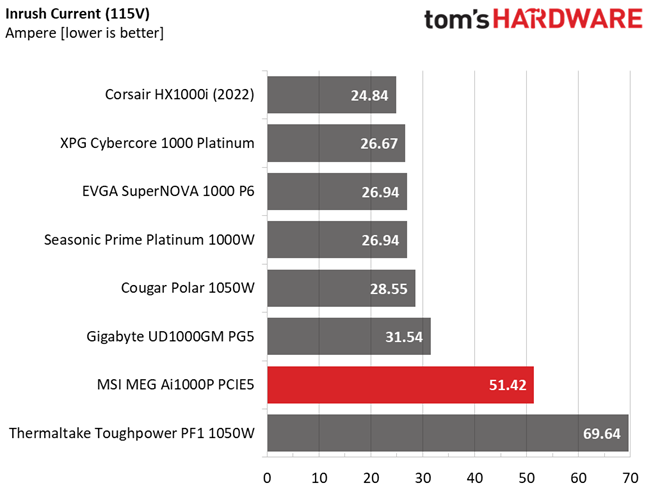
Inrush current is low with 230V input, but pretty high with 115V.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
Leakage Current
In layman's terms, leakage current is the unwanted transfer of energy from one circuit to another. In power supplies, it is the current flowing from the primary side to the ground or the chassis, which in the majority of cases is connected to the ground. For measuring leakage current, we use a GW Instek GPT-9904 electrical safety tester instrument.
The leakage current test is conducted at 110% of the DUT's rated voltage input (so for a 230-240V device, we should conduct the test with 253-264V input). The maximum acceptable limit of a leakage current is 3.5 mA and it is defined by the IEC-60950-1 regulation, ensuring that the current is low and will not harm any person coming in contact with the power supply's chassis.
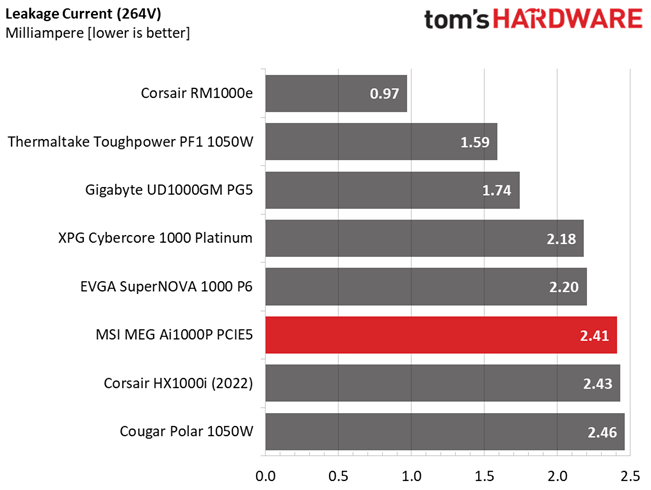
Leakage current is low.
10-110% Load Tests
These tests reveal the PSU's load regulation and efficiency levels under high ambient temperatures. They also show how the fan speed profile behaves under increased operating temperatures.
| Test | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed (RPM) | PSU Noise (dB[A]) | Temps (In/Out) | PF/AC Volts |
| 10% | 6.530A | 1.974A | 1.979A | 0.99A | 99.994 | 85.609% | 0 | <6.0 | 44.53°C | 0.979 |
| Row 2 - Cell 0 | 12.006V | 5.066V | 3.334V | 5.053V | 116.82 | Row 2 - Cell 6 | Row 2 - Cell 7 | Row 2 - Cell 8 | 40.19°C | 115.13V |
| 20% | 14.083A | 2.963A | 2.97A | 1.189A | 199.944 | 90.96% | 0 | <6.0 | 45.41°C | 0.993 |
| Row 4 - Cell 0 | 12.003V | 5.062V | 3.333V | 5.048V | 219.779 | Row 4 - Cell 6 | Row 4 - Cell 7 | Row 4 - Cell 8 | 40.58°C | 115.1V |
| 30% | 22.029A | 3.459A | 3.465A | 1.388A | 299.991 | 91.918% | 0 | <6.0 | 46.59°C | 0.996 |
| Row 6 - Cell 0 | 11.982V | 5.06V | 3.333V | 5.044V | 326.286 | Row 6 - Cell 6 | Row 6 - Cell 7 | Row 6 - Cell 8 | 41.47°C | 115.08V |
| 40% | 29.922A | 3.955A | 3.96A | 1.588A | 399.623 | 92.367% | 0 | <6.0 | 47.24°C | 0.997 |
| Row 8 - Cell 0 | 11.978V | 5.057V | 3.333V | 5.039V | 432.642 | Row 8 - Cell 6 | Row 8 - Cell 7 | Row 8 - Cell 8 | 41.62°C | 115.05V |
| 50% | 37.485A | 4.947A | 4.951A | 1.788A | 499.353 | 92.349% | 0 | <6.0 | 48.83°C | 0.997 |
| Row 10 - Cell 0 | 11.974V | 5.054V | 3.332V | 5.034V | 540.71 | Row 10 - Cell 6 | Row 10 - Cell 7 | Row 10 - Cell 8 | 42.83°C | 115.02V |
| 60% | 45.213A | 5.941A | 5.944A | 1.989A | 599.904 | 91.849% | 786 | 13.3 | 43.66°C | 0.997 |
| Row 12 - Cell 0 | 11.946V | 5.051V | 3.331V | 5.029V | 653.12 | Row 12 - Cell 6 | Row 12 - Cell 7 | Row 12 - Cell 8 | 50.24°C | 114.99V |
| 70% | 52.835A | 6.936A | 6.938A | 2.19A | 699.632 | 91.291% | 1146 | 25.4 | 44.13°C | 0.997 |
| Row 14 - Cell 0 | 11.934V | 5.047V | 3.33V | 5.023V | 766.378 | Row 14 - Cell 6 | Row 14 - Cell 7 | Row 14 - Cell 8 | 51.14°C | 114.97V |
| 80% | 60.507A | 7.934A | 7.932A | 2.292A | 799.673 | 90.681% | 1493 | 34.7 | 44.48°C | 0.999 |
| Row 16 - Cell 0 | 11.929V | 5.043V | 3.328V | 5.019V | 881.889 | Row 16 - Cell 6 | Row 16 - Cell 7 | Row 16 - Cell 8 | 52.58°C | 114.96V |
| 90% | 68.587A | 8.434A | 8.416A | 2.393A | 899.47 | 90.043% | 1792 | 39.4 | 44.85°C | 0.999 |
| Row 18 - Cell 0 | 11.911V | 5.039V | 3.326V | 5.014V | 998.961 | Row 18 - Cell 6 | Row 18 - Cell 7 | Row 18 - Cell 8 | 54.17°C | 114.92V |
| 100% | 76.422A | 8.938A | 8.93A | 3A | 999.511 | 89.529% | 2079 | 43.2 | 45.62°C | 0.998 |
| Row 20 - Cell 0 | 11.905V | 5.035V | 3.325V | 5V | 1117.686 | Row 20 - Cell 6 | Row 20 - Cell 7 | Row 20 - Cell 8 | 55.69°C | 114.9V |
| 110% | 84.195A | 9.939A | 10.017A | 3.002A | 1100.128 | 88.743% | 2326 | 47.0 | 46.78°C | 0.998 |
| Row 22 - Cell 0 | 11.899V | 5.031V | 3.324V | 4.998V | 1239.721 | Row 22 - Cell 6 | Row 22 - Cell 7 | Row 22 - Cell 8 | 57.71°C | 114.87V |
| CL1 | 0.117A | 14.26A | 14.322A | 0A | 121.295 | 83.348% | 698 | 8.7 | 42.95°C | 0.985 |
| Row 24 - Cell 0 | 11.994V | 5.063V | 3.33V | 5.086V | 145.539 | Row 24 - Cell 6 | Row 24 - Cell 7 | Row 24 - Cell 8 | 48.88°C | 115.13V |
| CL2 | 0.116A | 21.715A | 0A | 0A | 111.386 | 81.875% | 1285 | 29.4 | 43.56°C | 0.983 |
| Row 26 - Cell 0 | 12.007V | 5.065V | 3.333V | 5.109V | 136.12 | Row 26 - Cell 6 | Row 26 - Cell 7 | Row 26 - Cell 8 | 50.64°C | 115.13V |
| CL3 | 0.116A | 0A | 21.794A | 0A | 73.986 | 74.395% | 1370 | 31.7 | 44.31°C | 0.837 |
| Row 28 - Cell 0 | 12.022V | 5.067V | 3.331V | 5.059V | 99.443 | Row 28 - Cell 6 | Row 28 - Cell 7 | Row 28 - Cell 8 | 52.49°C | 115.15V |
| CL4 | 83.927A | 0A | 0A | 0A | 1000.076 | 90.096% | 2058 | 42.8 | 45.97°C | 0.998 |
| Row 30 - Cell 0 | 11.916V | 5.041V | 3.33V | 5.046V | 1112.815 | Row 30 - Cell 6 | Row 30 - Cell 7 | Row 30 - Cell 8 | 55.92°C | 114.9V |
The PSU delivered 1,100 wats of load at close to 47 degrees Celsius without any issues, but you should not over-stress it if you want it to outlive the extended warranty. The cooling fan rotated at full speed only during the overload test.
20-80W Load Tests
In the following tests, we measure the PSU's efficiency at loads significantly lower than 10% of its maximum capacity (the lowest load the 80 Plus standard measures). This is important for representing when a PC is idle with power-saving features turned on.
| Test | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed (RPM) | PSU Noise (dB[A]) | Temps (In/Out) | PF/AC Volts |
| 20W | 1.236A | 0.493A | 0.495A | 0.197A | 19.996 | 73.387% | 0 | <6.0 | 40.23°C | 0.687 |
| Row 2 - Cell 0 | 12.019V | 5.068V | 3.335V | 5.067V | 27.316 | Row 2 - Cell 6 | Row 2 - Cell 7 | Row 2 - Cell 8 | 37.09°C | 115.15V |
| 40W | 2.723A | 0.691A | 0.693A | 0.296A | 39.994 | 75.323% | 0 | <6.0 | 41.24°C | 0.791 |
| Row 4 - Cell 0 | 12.003V | 5.067V | 3.334V | 5.064V | 53.123 | Row 4 - Cell 6 | Row 4 - Cell 7 | Row 4 - Cell 8 | 37.79°C | 115.15V |
| 60W | 4.210A | 0.888A | 0.89A | 0.395A | 59.992 | 79.229% | 0 | <6.0 | 41.74°C | 0.818 |
| Row 6 - Cell 0 | 12.002V | 5.067V | 3.335V | 5.063V | 75.588 | Row 6 - Cell 6 | Row 6 - Cell 7 | Row 6 - Cell 8 | 38.05°C | 115.14V |
| 80W | 5.682A | 1.085A | 1.088A | 0.494A | 79.942 | 81.888% | 0 | <6.0 | 43.29°C | 0.836 |
| Row 8 - Cell 0 | 12.021V | 5.067V | 3.335V | 5.062V | 97.633 | Row 8 - Cell 6 | Row 8 - Cell 7 | Row 8 - Cell 8 | 39.31°C | 115.14V |
Efficiency under light loads should be higher. We would like to see three out of four tests with over 80% efficiency.
2% or 10W Load Test
From July 2020, the ATX spec requires 70% and higher efficiency with 115V input. The applied load is only 10W for PSUs with 500W and lower capacities, while for stronger units, we dial 2% of their max-rated capacity.
| 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | Fan Speed (RPM) | PSU Noise (dB[A]) | Temps (In/Out) | PF/AC Volts |
| 1.472A | 0.255A | 0.255A | 0.053A | 20.115 | 73.301% | 0 | <6.0 | 25.77°C | 0.678 |
| Row 2 - Cell 0 | 12.032V | 5.06V | 3.326V | 5.061V | 27.451 | Row 2 - Cell 6 | Row 2 - Cell 7 | 23.78°C | 115.15V |
With super-light loads, the platform delivers high efficiency.
Efficiency & Power Factor
Next, we plotted a chart showing the PSU's efficiency at low loads and loads from 10 to 110% of its maximum rated capacity. The higher a PSU’s efficiency, the less energy goes wasted, leading to a reduced carbon footprint and lower electricity bills. The same goes for Power Factor.
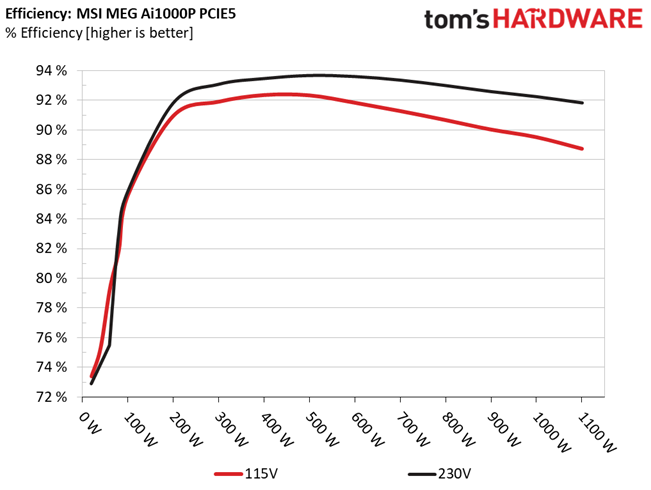
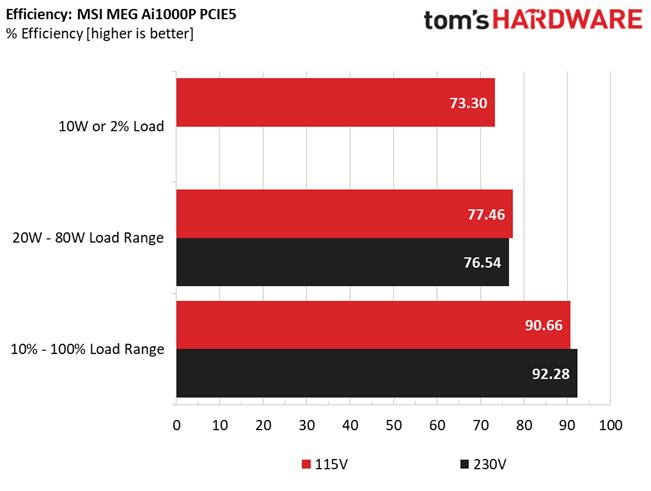
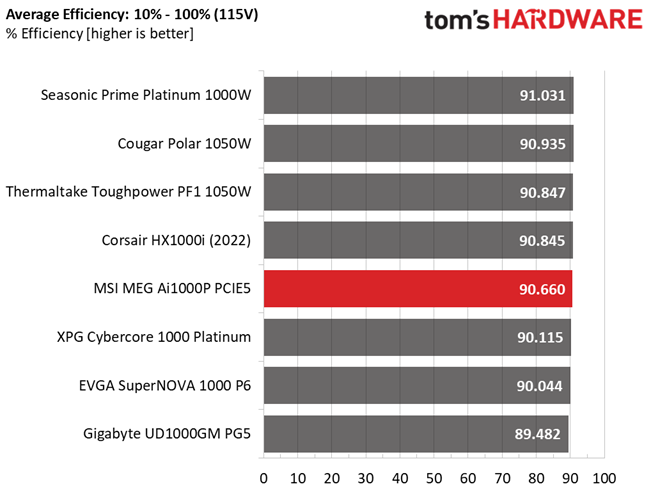
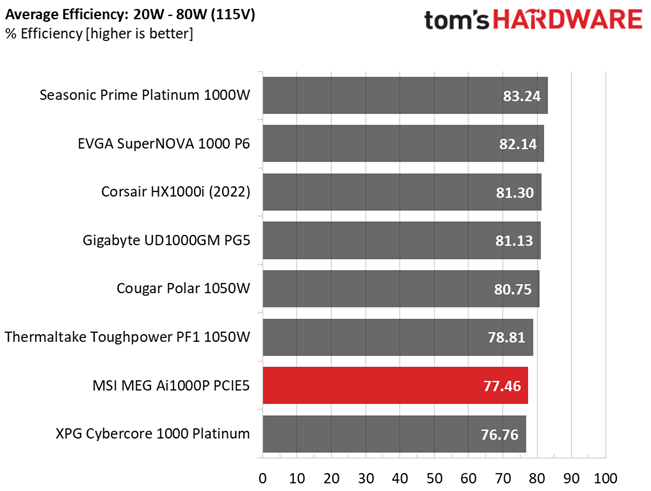
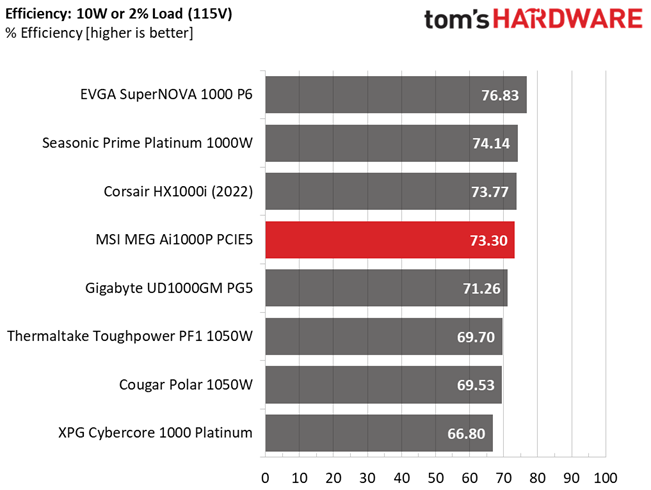
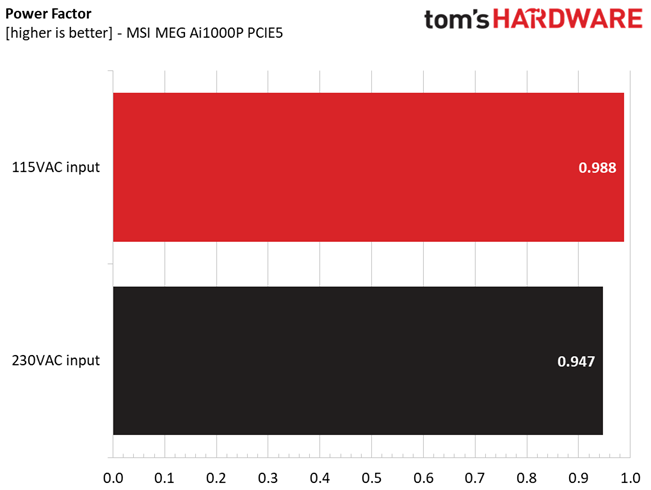
Efficiency is high enough with normal and super-light loads, but not so high with light loads. Moreover, the APFC converter needs tuning for higher PF readings with 230V input.
5VSB Efficiency
| Test # | 5VSB | DC/AC (Watts) | Efficiency | PF/AC Volts |
| 1 | 0.1A | 0.511W | 76.183% | 0.053 |
| Row 2 - Cell 0 | 5.108V | 0.671W | Row 2 - Cell 3 | 115.16V |
| 2 | 0.25A | 1.276W | 78.775% | 0.123 |
| Row 4 - Cell 0 | 5.104V | 1.62W | Row 4 - Cell 3 | 115.16V |
| 3 | 0.55A | 2.804W | 79.183% | 0.235 |
| Row 6 - Cell 0 | 5.097V | 3.541W | Row 6 - Cell 3 | 115.15V |
| 4 | 1A | 5.087W | 79.344% | 0.339 |
| Row 8 - Cell 0 | 5.086V | 6.411W | Row 8 - Cell 3 | 115.15V |
| 5 | 1.5A | 7.612W | 79.897% | 0.398 |
| Row 10 - Cell 0 | 5.074V | 9.529W | Row 10 - Cell 3 | 115.16V |
| 6 | 3A | 15.111W | 78.062% | 0.482 |
| Row 12 - Cell 0 | 5.037V | 19.357W | Row 12 - Cell 3 | 115.15V |
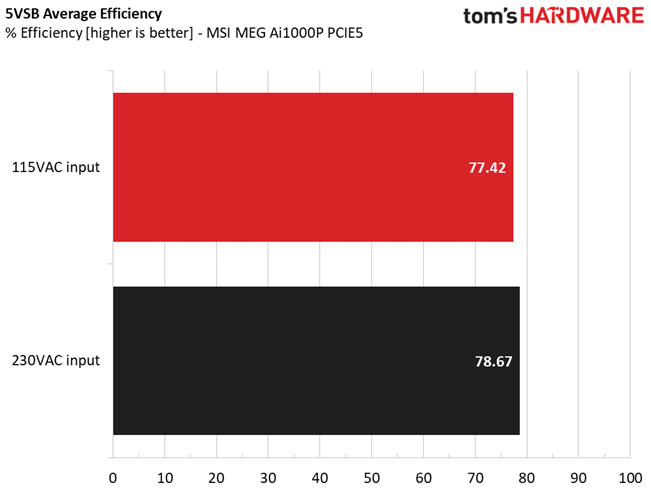
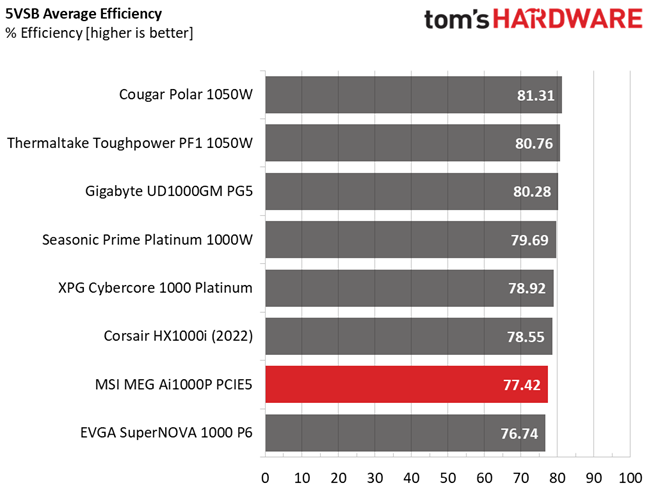
The 5VSB rail is not efficient and this is a great shame!
Power Consumption In Idle And Standby
| Mode | 12V | 5V | 3.3V | 5VSB | Watts | PF/AC Volts |
| Idle | 12.043V | 5.056V | 3.323V | 5.057V | 4.15 | 0.252 |
| Row 2 - Cell 0 | Row 2 - Cell 1 | Row 2 - Cell 2 | Row 2 - Cell 3 | Row 2 - Cell 4 | Row 2 - Cell 5 | 115.16V |
| Standby | Row 3 - Cell 1 | Row 3 - Cell 2 | Row 3 - Cell 3 | Row 3 - Cell 4 | 0.012 | 0.001 |
| Row 4 - Cell 0 | Row 4 - Cell 1 | Row 4 - Cell 2 | Row 4 - Cell 3 | Row 4 - Cell 4 | Row 4 - Cell 5 | 115.16V |
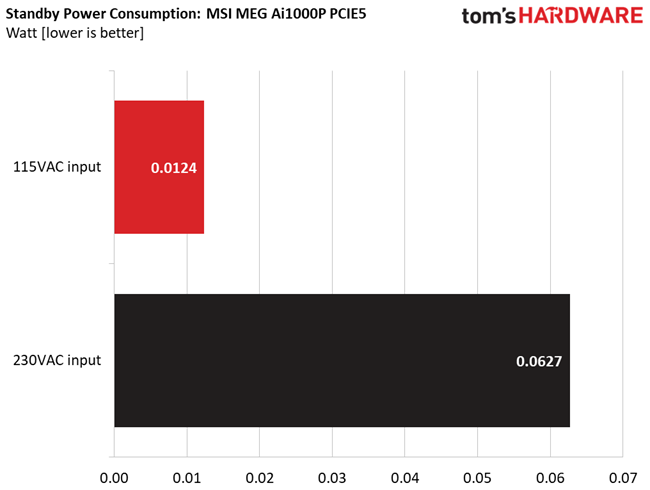
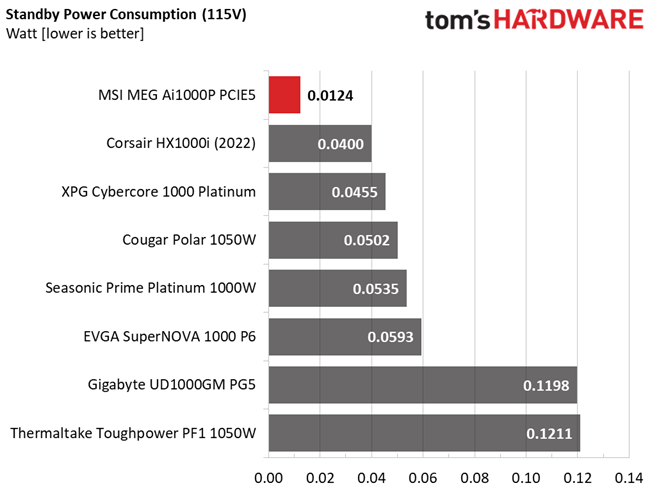
Vampire power is low.
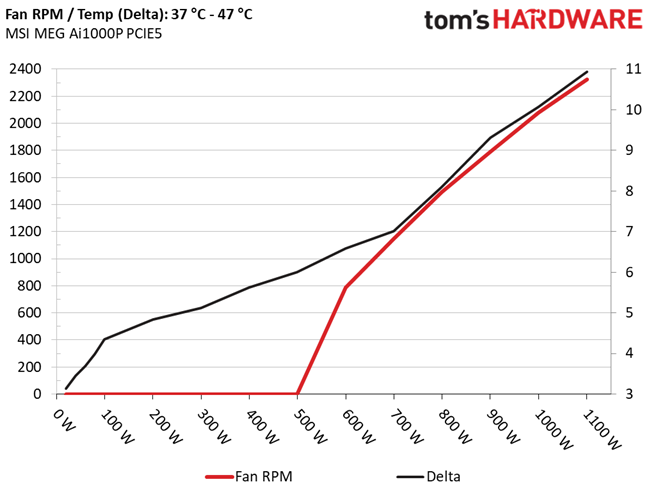
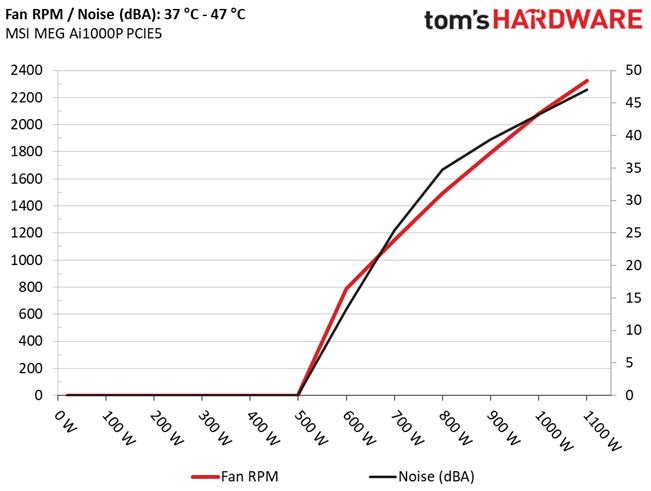
Fan RPM, Delta Temperature, And Output Noise
All results are obtained between an ambient temperature of 37 to 47 degrees Celsius (98.6 to 116.6 degrees Fahrenheit).
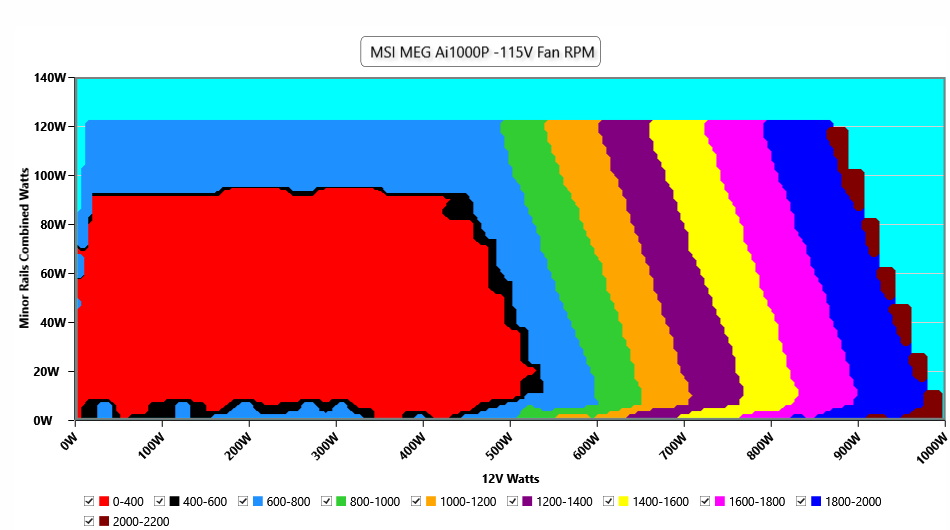
The fan speed profile is not aggressive, but the 120mm fan has to spin at high speeds under harsh conditions, to handle the thermal loads.
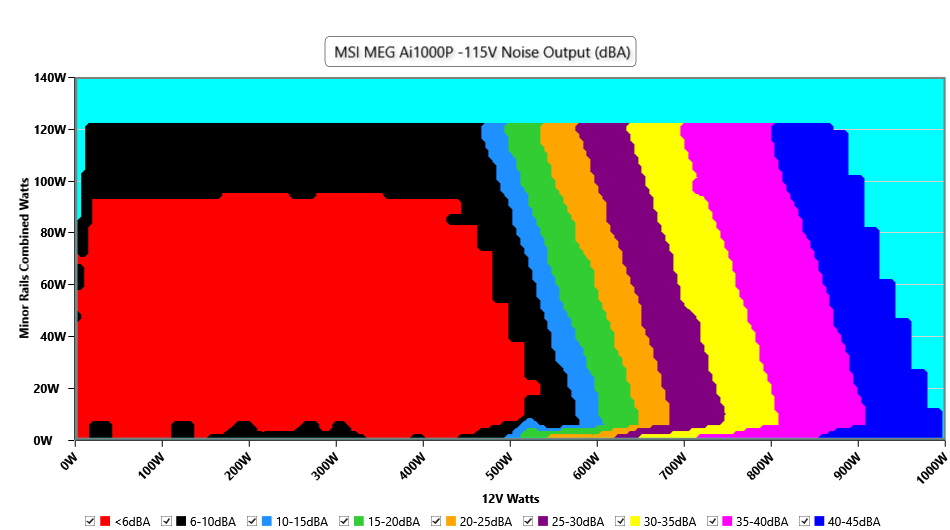
The following results were obtained at 30 to 32 degrees Celsius (86 to 89.6 degrees Fahrenheit) ambient temperature.
At normal operating temperatures, close to 30 degrees Celsius, the PSU is silent with up to 500W loads. With more than 650W at it enters the 30-35 dBA zone and the 40 dBA mark is passed with 860W and higher loads. As we already stated, with a larger fan, noise output could be lower at high loads.
MORE: Best Power Supplies
MORE: How We Test Power Supplies
MORE: All Power Supply Content
Current page: Load Regulation, Hold-Up Time, Inrush & Leakage Current, Efficiency and Noise
Prev Page Specifications and Part Analysis Next Page Protection Features, DC Power Sequencing, Cross-Load Tests and Infrared Images
Aris Mpitziopoulos is a contributing editor at Tom's Hardware, covering PSUs.
-
tummybunny Thanks for a fantastic and very detailed review. Something that isn't mentioned though is one of the really interesting new features of ATX 3.0.Reply
https://www.techpowerup.com/292563/intel-atx-3-0-16-pin-power-connector-for-pcie-gen5-is-smart-has-four-power-delivery-variants?cp=2
"The 12VHPWR connector has 12 electrical pins and 4 side-band pins, for a total of 16 pins. The side-band pins enable low-fi communication between the power-supply and the graphics card, and two of these pins, labeled "SENSE0" and "SENSE1," let the graphics card know what kind of connector is plugged in, so it can accordingly adjust its power-management."
What difference does this make to GPU performance? Perhaps you could argue it's something better discussed in a GPU review but I would like to hear about it one way or another. -
Hresna Great PSU coverage… although the standard formula I think misses some aspects of a complete review…Reply
For instance this model offers an MSI feature they all “gaming intelligence” via the USB connector… no mention of this in the article or how it works, what it does.
I’ve been a longtime fan of Corsairs ‘i’ series which also use USB as the enabler, for the simple fact that it gives power output readings in hwinfo64 which is a fanstastic tool for dialing in power budgets, overclocks/undervolts, or just… those of us who like numbers and data. I can do without the iCUe software, which thankfully isn’t needed for this.
Does MSI’s GI do that also?
It’s extremely difficult to find PSU models with these sorts of features. At least the ‘i’ thing seems to be catching on and might serve as a semi-reliable indicator between manufacturers. -
halfcharlie ReplyHresna said:For instance this model offers an MSI feature they all “gaming intelligence” via the USB connector… no mention of this in the article or how it works, what it does.
What's this on the first page then?
"there is compatibility with the MSI Gaming Intelligence application, through which you can adjust several settings, like the fan's speed and toggle on/off the single +12V mode while monitoring the PSU's vital functions and power delivery. " Also google exists. -
CheckYourFacts The Author asserts: "The four main FETs are installed into a full-bridge topology. " Where does he get that information from when the vendor says its a "LLC Half Bridge Topology with DC-DC module design "Reply
https://www.msi.com/Power-Supply/MEG-Ai1000P-PCIE5 -
bignastyid Reply
Considering Aris is one of the top experts/reviewers in PSUs and he did a teardown. I'd believe him over the advertised specs any day.CheckYourFacts said:The Author asserts: "The four main FETs are installed into a full-bridge topology. " Where does he get that information from when the vendor says its a "LLC Half Bridge Topology with DC-DC module design "
https://www.msi.com/Power-Supply/MEG-Ai1000P-PCIE5 -
CheckYourFacts Replybignastyid said:Considering Aris is one of the top experts/reviewers in PSUs and he did a teardown. I'd believe him over the advertised specs any day.
This is not about the authors reputation, which i know nothing about. It is about journalistic work ethics, his claim is in clear contradiction to the vendor claims. -
bignastyid Reply
He opened it up and wrote what he found. If anything that would put the companies ethics in question not the reviewers.CheckYourFacts said:This is not about the authors reputation, which i know nothing about. It is about journalistic work ethics, his claim is in clear contradiction to the vendor claims. -
Lutfij Reply
You might want to do a bit of digging and see what Kingston did within the last decade. If you can't find it, I'll help you;CheckYourFacts said:This is not about the authors reputation, which i know nothing about. It is about journalistic work ethics, his claim is in clear contradiction to the vendor claims.
Kingston sent out SSD's to practically every reviewer known to the (tech)community and once sales drove up to remove practically all units off the shelves, people all stated how the speeds weren't the same as seen by reviewers in spite of the advertised material stating otherwise. A further digging by TekSyndicate/Level1 found out about how cherry picked samples were handed out to help garner a better image.
That being said, please stop with the needless jabbing, the question falls onto the brand that sent the review sample out, not the person who opened up the unit to report what he'd seen. You're also talking about Aris, here. You're sneezing towards the wind.
If you believe everything that the brand's marketing material states, then AIO coolers MSI released were the best coolers in the world, not the market, the world. -
Hresna Reply
Okay so I missed that brief description.halfcharlie said:What's this on the first page then?
"there is compatibility with the MSI Gaming Intelligence application, through which you can adjust several settings, like the fan's speed and toggle on/off the single +12V mode while monitoring the PSU's vital functions and power delivery. " Also google exists.
And yes google exists, but my point was, in a review for something, if you’re going to mention a unique feature - something that sets it apart from its competition - might be worthwhile including a fulsome description and reviewing its functionality.
So I retract that it wasn’t described at all.