Overclocking Intel’s Xeon E5620: Quad-Core 32 nm At 4+ GHz
Power And Heat
To be honest, I didn’t tackle all of those benchmarks thinking that Intel’s Xeon E5620 was going to somehow magically outperform a six-core desktop chip. I also didn’t think 4 MB of additional L3 cache was going to put a huge lead over the 45 nm Bloomfield design, with its 8 MB repository.
Rather, I was hoping to see higher frequencies at lower operating temperatures, perhaps with a little power-savings sprinkled on top.
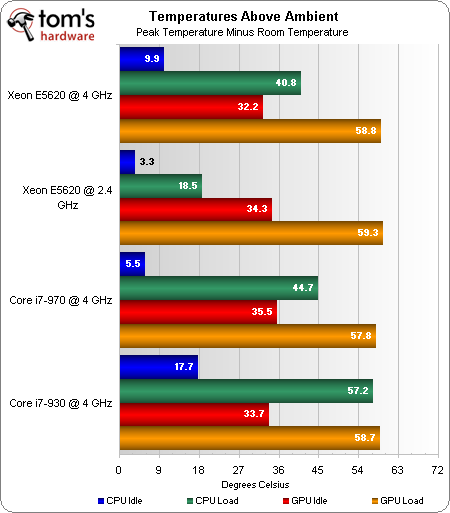
I took ambient temperature readings in between each result using an Extech TM200 thermometer. You can disregard those orange and red bars—the GPU remains fairly consistent at idle and load, regardless of the processor behind it. More interesting are the blue and green bars.
It comes as little surprise that the stock Xeon E5620 is an example of low thermal output thanks to conservative clocks and low operating voltage.
The overclocked Xeon runs significantly warmer due to a 1.6 GHz frequency increase and a higher fixed voltage.
Two additional cores mean that the Core i7-970 gets hotter still—about 10% warmer than the quad-core Xeon.
And an older manufacturing process translates to significantly hotter idle and load temperatures for the overclocked Core i7-930. And when you consider the ambient temp hovered around 32 degrees in my lab, adding 57 to that sticks the loaded Bloomfield core up around 90 degrees. That’s uncomfortably warm, long-term. In fact, I’d probably recommend dialing back to 3.73 GHz or so and dialing back voltage a bit in order to hopefully get a little more useful life out of the chip.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
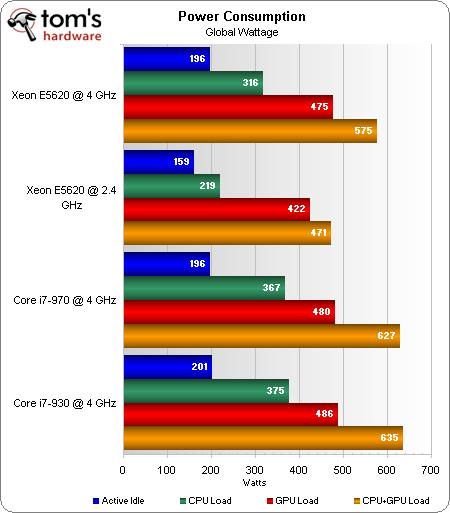
At idle, the overclocked Gulftown-based processors use the same amount of power. The stock Xeon is quite a bit more conservative with its consumption. And the Core i7-930 is only moderately higher than the other 4 GHz CPUs.
Load the CPUs down, though, and you get another story entirely. The stock Xeon E5620 is still fairly power-friendly. Overclocked and overvolted, consumption rises by nearly 100 W. Yet, the Xeon E5620 still uses 50 W less than the overclocked Core i7-970. And the Xeon uses roughly 60 W less than the other overclocked quad-core chip in this comparison, Intel’s Core i7-930.
Those results translate over to CPU+GPU power measurements, too. The overclocked Xeon E5620 uses 60 W less than the 4 GHz Core i7-930 setup. So, you’re getting roughly the same performance, significant power savings, and less heat output for a $100 price premium.
Current page: Power And Heat
Prev Page Benchmark Results: Productivity Next Page Efficiency And Value Analysis-
intelx i wish it had higher multiplier it would of been a great processor to recommend than paying $10000 for the i7 970.Reply -
JOSHSKORN I wonder if it's possible and also if it'd be useful to do a test of various server configurations for game hosting. Say for instance we want to build a game server and don't know what parts are necessary for the amount of players we want to support without investing too much into specifications we don't necessarily need. Like say I hosted a 64-player server of Battlefield or CoD or however the max amount of players are. Would a Core i7 be necessary or would a Dual-Core do the job with the same overall player experience? Would also want to consider other variables: memory, GPU. I realize results would also vary depending on the server location, its speed, and the player's location and speed, too, along with their system's specs.Reply -
cangelini JOSHSKORNI wonder if it's possible and also if it'd be useful to do a test of various server configurations for game hosting. Say for instance we want to build a game server and don't know what parts are necessary for the amount of players we want to support without investing too much into specifications we don't necessarily need. Like say I hosted a 64-player server of Battlefield or CoD or however the max amount of players are. Would a Core i7 be necessary or would a Dual-Core do the job with the same overall player experience? Would also want to consider other variables: memory, GPU. I realize results would also vary depending on the server location, its speed, and the player's location and speed, too, along with their system's specs.Reply
Josh, if you have any ideas on testing, I'm all ears! We're currently working with Intel on server/workstation coverage (AMD has thus far been fairly unreceptive to seeing its Opteron processors tested).
Regards,
Chris -
You could setup a small network with very fast LAN speeds (10Gbps maybe?). You can test ping and responsiveness on the clients, and check CPU/memory usage on the server. Eliminating the bottleneck of the connection and testing many different games with dedicated servers one can actually get a good idea of what is needed to eliminate bottlenecks produced by the hardware itself.Reply
-
Moshu78 Dear Chris,Reply
thank you for the review but your benchmarks prove that you were GPU-bottlenecked almost all time.
Letme explain: i.e. Metro 2033 or Just Cause 2... the Xenon running at 2.4 GHz provided the same FPS as when it ran at 4 GHz. That means your GPU is the bottleneck since the increase in CPU speed therefore the increase in the number of frames sent to the GPU for processing each second does not produce any visible output increase... so the GPU has too much to process already.
I also want to point out that enabling the AA and AF in CPU tests puts additional stress on the GPU therefore bottlenecking the system even more. It should be forbidden to do so... since your goal is to thest the CPU not the GPU.
Please try (and not only you, there is more than 1 article at Tom's) so try to reconsider the testing methodology, what bottleneck means and how can you detect it and so on...
Since the 480 bottlenecked most of the gaming results are useless except for seeing how many FPS does a GF480 provide in games, resolutions and with AA/AF. But that wasn't the point of the article.
LE: missed the text under the graphs... seems you are aware of the issue. :) Still would like to see the CPU tests performed on more GPU muscle or on lower resolutions/older games. This way you'll be able to get to the real interesting part: where/when does the CPU bottleneck? -
Looks to me to be a pointless exercise. I have been running an i7-860 @ 4.05 Ghz and low temps for more than a year now so why pay for a motherboard that expensive plus the chip?Reply
-
Cryio I have a question. Maybe two. First: Since when Just Cause 2 is a DX11 game? I knew it was only DX10/10.1 . And even if it is , what are the differences between the DX10 and 11 versions?Reply -
omoronovo blibbaNote: Higher clocked Xeons are available.Reply
However, I'm sure everyone is aware of how sharply the price of Xeons rise above the lowest-of-the-low. I expect a Xeon capable of 4.5ghz (a good speed to aim for with a 32nm chip and good cooling), you would already be over the costs of purchasing a 970/980x/990x, especially considering how good a motherboard you would need to get - a Rampage III extreme is possibly one of the most expensive X58 boards on the market, offsetting most of the gains you'd get over a 45nm chip and a more wallet friendly board - such as the Gigabyte GA-X58A-UD3R. -
compton This is one of the best articles in some time. I went AMD with the advent of the Phenom IIs despite never owning or using them previously, and I didn't once long going back to Intel for my processor needs. But I think that may have changed with the excellent 32nm products. The 980X might be the cat's pajamas, but $1000 is too much unless you KNOW you need it (like 3x SLI 480s, or actual serious multithreaded workloads when TIME = $$$). The lowly i3 has seriously impressed the hell out of me for value/performance, heat, and price/performance. Now, this Xeon rears it's head. While still pricey in absolute terms, it is still a great value play. Intel has earned my business back with their SSDs -- now might be the time to get back in on their processors, even if Intel's content to keep this chip in the Xeon line. Thanks for the illumination.Reply