Extreme Overclocking: 10 Ryzen CPUs Under LN2
OC: Ryzen 5 1600X & 1600
We have two processors endowed with six cores and two others with four. Which one will overclock the best? Now's the time to place your bets.
Ryzen 5 1600X: 5250 MHz
During our air cooling tests, the 1600X wouldn't cooperate. Bugs kept popping up and holding back the frequency. We assumed things would get worse once we introduced LN2. In the end, while our sample didn't have any issues with liquid nitrogen cooling specifically, it still proved difficult to get running.
At this point, it's pretty safe to conclude that you never know what you're going to get. The behavior of these processors is much too variable from one to the next, even among identical models.
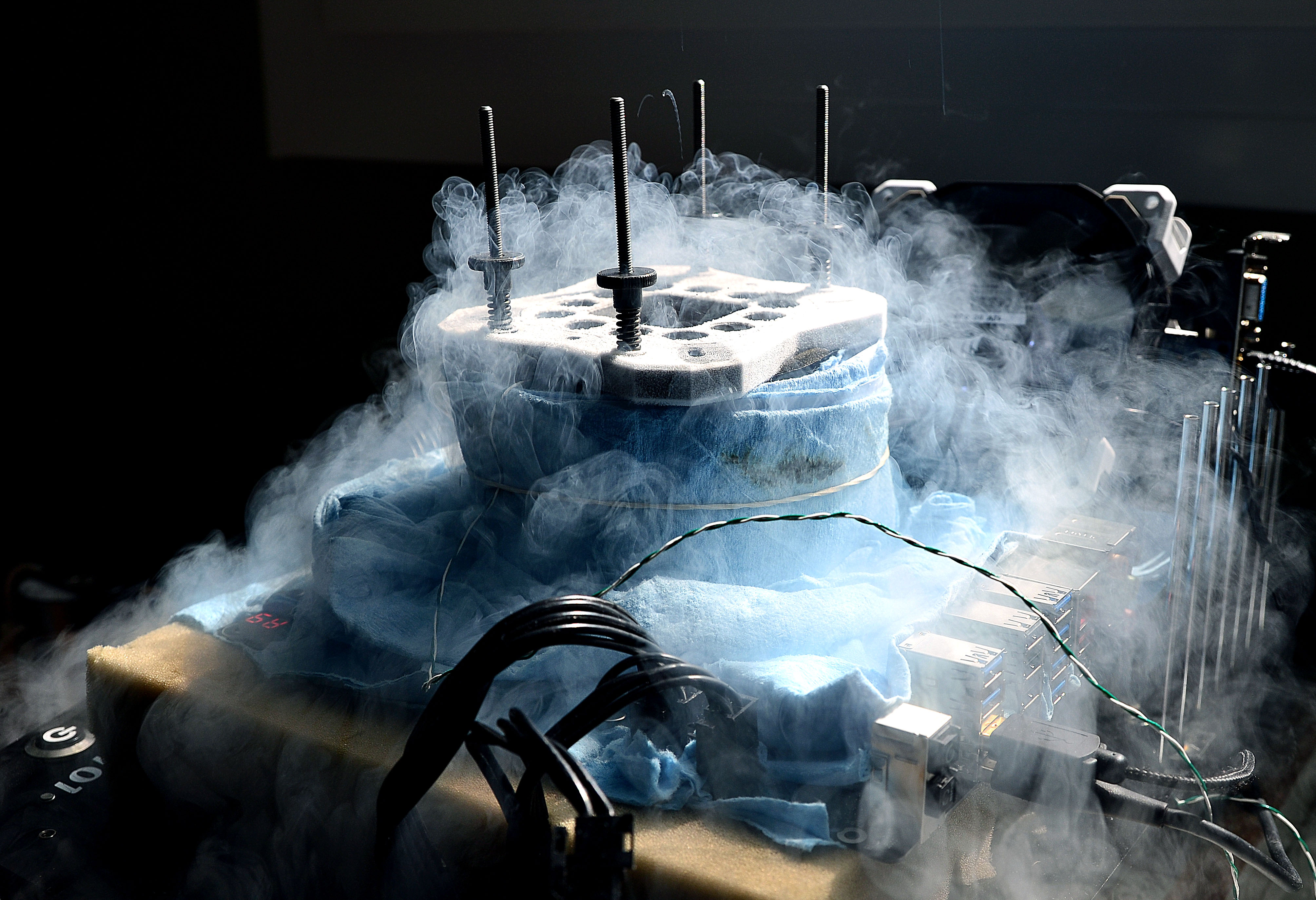
After spending two hours with LN2, we only saw Windows twice. Two times in as many hours is a poor showing, to say the least, which explains the absence of a score.
We hit 5.1 GHz at 1.7V, and even saw 5250 MHz once at 1.85V. The cores are pretty good, but far from Der8auer's diamond in the rough that exceeds 5.4 GHz. Still, the clock rate we recorded was good enough to land second-highest for a Ryzen 5.
For reasons pertaining to our mental health, we didn't bother trying to squeeze any more performance from the processor's memory controller.
At the end of this chip's trials, as we were removing the cooling pot, our Ryzen 5 1600X got stuck to the bottom and was pulled from its socket. This isn't the first time we've seen that. Either the socket doesn't grip tightly enough, or the thermal paste has too much suction. Fortunately, nothing was damaged.
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.
R5 1600: 5075 MHz
Unlike the six-core chips we just finished testing, our 1600 didn't suffer any show-stopping bugs. Whether it be air or LN2 cooling, its behavior is normal. This processor loves high core voltages and exhibits progression up to 1.92V. With that said, it's not a great performer, plateauing at 5075 MHz. The IMC is nothing exceptional; we timidly reached 3000 MT/s at CAS 12, but were stable around 2800 MT/s for our memory-intensive benchmarks.
This doesn't mean that all 1600s will behave this way. We'd guess that fewer active cores would enable higher maximum clock rates. But that doesn't prove to be the case today.
MORE: Best CPUs
MORE: How To Overclock AMD Ryzen CPUs
MORE: De-Lidding and Overclocking Core i7-7700K
MORE: CPU Overclocking Guide: How (and Why) to Tweak Your Processor
Current page: OC: Ryzen 5 1600X & 1600
Prev Page OC: Ryzen 7 1700X & 1700 Next Page OC: Ryzen 5 1500X & 1400-
InvalidError It isn't surprising that the highest-end CPUs have the highest and least troublesome overclocks as that's what chip binning is for - the best dies go to the premium SKUs first, lower tiers get what is left over.Reply -
-Fran- Reply19937674 said:It isn't surprising that the highest-end CPUs have the highest and least troublesome overclocks as that's what chip binning is for - the best dies go to the premium SKUs first, lower tiers get what is left over.
Even more, it's very interesting since it gives some credibility that AMD is not binning due to defects, but electrical properties, hence, making the rumour mill of being able to unlock some 4C and 6C to higher core counts not that far-fetched.
Cheers! -
Wisecracker Très bon!Reply
(hope I used this correctly)
Just wondering ... would it be considered a 'faux pas' (or, an insult to AMD) to release the batch numbers?
-
theyeti87 Reply19937697 said:19937674 said:It isn't surprising that the highest-end CPUs have the highest and least troublesome overclocks as that's what chip binning is for - the best dies go to the premium SKUs first, lower tiers get what is left over.
Even more, it's very interesting since it gives some credibility that AMD is not binning due to defects, but electrical properties, hence, making the rumour mill of being able to unlock some 4C and 6C to higher core counts not that far-fetched.
Cheers!
Wasn't that a similar case with the Phenom X4, X3, and X2's? Or were those 3's and 2's disabled cores due to defect? -
-Fran- Reply19937706 said:19937697 said:19937674 said:It isn't surprising that the highest-end CPUs have the highest and least troublesome overclocks as that's what chip binning is for - the best dies go to the premium SKUs first, lower tiers get what is left over.
Even more, it's very interesting since it gives some credibility that AMD is not binning due to defects, but electrical properties, hence, making the rumour mill of being able to unlock some 4C and 6C to higher core counts not that far-fetched.
Cheers!
Wasn't that a similar case with the Phenom X4, X3, and X2's? Or were those 3's and 2's disabled cores due to defect?
They were a mix of both. If you were lucky (and could track down some of the batches) you were able to unlock the CPU with little worry, but there were defective ones that when unlocked, would not work. I came across both myself.
To be honest, I just catalog it as "interesting", because I will pay the difference to always get the full working version, but I do know there's people out there that like gambling and can track batch numbers :P
Cheers! -
InvalidError Reply
The relatively low defect rate has been a given since launch IMO: half of each CPU core is L2 cache and half of the CCX die area is the L3, so you have a 50% chance that defects within a CCX will land in L3. If the defect rate had been significant, cache defects would have forced AMD to launch models with 8MB of L3 long before the 1400.19937697 said:Even more, it's very interesting since it gives some credibility that AMD is not binning due to defects, but electrical properties -
-Fran- Reply19937880 said:
The relatively low defect rate has been a given since launch IMO: half of each CPU core is L2 cache and half of the CCX die area is the L3, so you have a 50% chance that defects within a CCX will land in L3. If the defect rate had been significant, cache defects would have forced AMD to launch models with 8MB of L3 long before the 1400.19937697 said:Even more, it's very interesting since it gives some credibility that AMD is not binning due to defects, but electrical properties
True. It's just nice to have more non-validated statistical-irrelevant proof! Haha.
Cheers! :P -
Gregory_3 This is all kind of cute, but the real market success will be played out in conventional liquid cooled and air cooled environments. Nobody is going be running high end software with condensation dripping all over.Reply -
InvalidError Reply
There wouldn't be condensation issues if OCers used the nitrogen gas boiling out of the pot to displace air and the moisture it contains around the motherboard to keep it off of it. Instead of circulating the boil-off around the motherboard though, LN2 OCers use fans to suck it away, drawing more moisture-ladden air in the area.19938043 said:Nobody is going be running high end software with condensation dripping all over.
-
gasaraki "It isn't surprising that the highest-end CPUs have the highest and least troublesome overclocks as that's what chip binning is for - the best dies go to the premium SKUs first, lower tiers get what is left over."Reply
While it might not be surprising, it shows the immaturity of the Ryzen processors in that the build quality is not the same between different CPUs or even CCXes and binning is what they do for the lower cored versions. If your build process was mature ALL your chips would come out mostly the same and "awesome" then at that point your forced to just shutdown cores to make the lower cored processors.